Helping fishermen reduce their impact
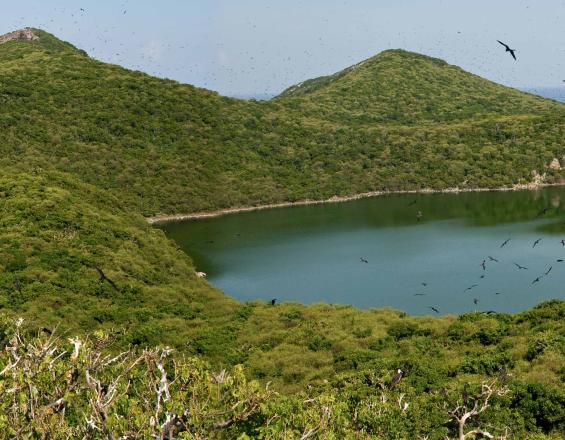

High levels of marine productivity around the National Park Isla Isabel attract fishermen, who have been using the island as a temporary camp site for almost 100 years. However, a steadily growing number of fishermen and a lack of organisation have increased the pressure on the island’s natural resources. CONANP initiated a participatory process with the local fishermen to improve the management of the fishing camp and ensure that all activities meet environmental regulations.
Contexte
Challenges addressed
- Unregulated use of the island by fishermen impacting biodiversity
- Conflicts between the island’s fishermen and national park operators
- Missing involvement of fishermen in the management of the island
- Governance of the island
Emplacement
Traiter
Summary of the process
Building Blocks
Consensus on natural resource use
Regular meetings with relevant stakeholders, including representatives from academia, governmental agencies, national park staff and local fishermen, promote consensus regarding directives for the use and protection of natural resources.
Enabling factors
tba
Lesson learned
tba
Management plan for the National Park
The conservation and management programme formalizes jointly agreed regulations. It contains various sub-programmes with defined objectives, actions and guidelines to improve the state of conservation and management.
Enabling factors
tba
Lesson learned
tba
Education campaigns
Environmental education campaigns raise awareness of issues associated with the fishing camp. Special emphasis is placed on the control of introduced species, waste management and outdoor defecation. Information is disseminated via various media.
Enabling factors
tba
Lesson learned
tba
Roles and responsibilities within National Parks
Roles and responsibilities are defined for all stakeholders. To achieve the required compliance with administrative rules, stakeholders are actively involved in inspection and surveillance activities. The violation of an agreement can result in temporary denial of access to the island.
Enabling factors
tba
Lesson learned
tba
Thematic workshops for fishermen
Workshops are conducted to increase local fishermen‘s capacities. These focus on conservation, sustainable fishing techniques, biosafety measures and solid waste management. Meetings with fishermen from other protected areas in the region, NGOs and research centres facilitate knowledge transfer.
Enabling factors
tba
Lesson learned
tba
Impacts
The regulation of camping condensed in the recovery of previously irritated vegetation zones e.g. by ceasing to use trees as firewood to prepare food. The exploitation of native birds and reptiles of the island and their products stopped. The placement of the camping side with 30 ecological latrines ended open air defecation. Residuals have been eliminated and the risk of human introduction of alien species has been reduced. Fishermen do now participate in the conservation of the island; these actions also have been extended to the surrounding marine area. The conflicts between the fishermen and with the national park’s personal are decreasing. Moreover, if conflicts are emerging now there exist adequate canals and norms to solve them. For the operators of the national park the regulation of the camping resulted in an improved and more efficient use of their own resources. For the fishermen the security to have temporary camping during fishing activities, in this case far away from the coast, means lower investment costs and an increase in their economic activities.
Beneficiaries
The general public, national park operators and fishermen as well as tourism operators, park visitors and researchers.
Story
»With the new management approach, things have become better regulated,« says Juan Dovora, fisherman in Isla Isabel. »There is no longer such an uncontrolled arrival of fishermen. This was achieved by the hard work of the staff of the park, of Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México (UNAM), and of the government, who were engaged in fostering our compliance to the new rules, which turned out to be really beneficial. When the management plan was being discussed, we did not want to miss that opportunity. Now we try to give something back – to the extent that we supported them, we also support ourselves. Today the park is already being revived with all the jobs that are being created.«