Restoring Balance: Recognizing Nature and Knowledge in Jaipur’s Heritage Through Research-Practice Collaboration
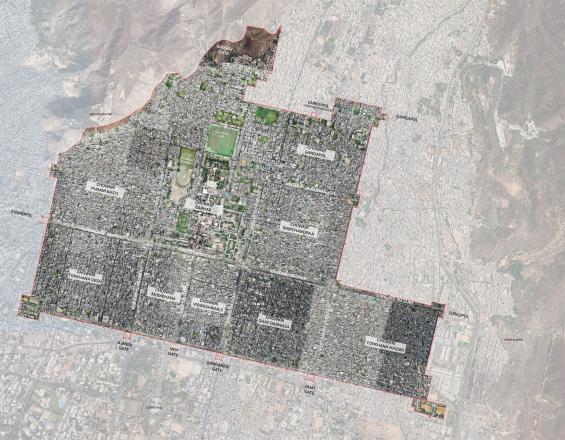

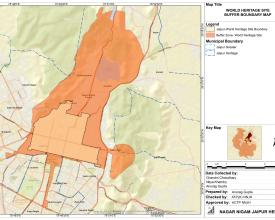
As a cultural World Heritage Site in an arid region of India, Jaipur city is experiencing pressures of a rapidly expanding human population and is susceptible to growing impact from climate change. To address some of the key issues faced by the city, the process established by a multidisciplinary research-practice team during the ICCROM-IUCN World Heritage Leadership Heritage Place Lab led to a wide-ranging, management needs-oriented research agenda which will add to the existing body of heritage conservation of Jaipur. The Heritage Place Lab promoted a cross functional collaboration between the Manipal University, Wildlife Institute of India Category 2 Centre and Jaipur Municipal Corporation and Town Planning, in which all institutions applied their respective expertise to (1) revise their individual approaches to heritage conservation and (2) to develop a common policy incorporating diverse points of view that may serve as a template for other teams, especially in the field of urban heritage.
Impacts
The first impact was to be able to identify the key challenges facing the property with inputs from the broader perspectives of different team members - conservation architects, academics, natural and cultural heritage researchers, town planning and urban management professionals - to be able to draw on the extensive natural features that underpin its historical location to frame more effective management questions and shortlist questions addressing the same.
The same mix of expertise and techniques led to the proposal that the wider aim of conservation of Indigenous traditional knowledge could be focused on what was of key importance to Jaipur. Hence the need for detailed research on traditional water management systems was identified. These systems had functioned very effectively when the city was first set up and could still offer ways to improve water management & contribute to achieving modern day water needs. A structured look through the archives of the historic urban development and architectural control guidelines would help in conservation of Jaipur’s heritage through identification and cataloguing of heritage records.
All of the above identified research priorities would lead to solutions which (1) preserve Jaipur’s extensive heritage and help promote it to the citizenry, and (2) cause impactful changes in the city’s living conditions and fulfil citizens’ present day needs.