International Alliance against Health Risks in Wildlife Trade

With increasing global human activity encroaching on wildlife habitats, growing demand for wildlife consumption & expanding global trade, the risk of pathogen spillover from wildlife to humans is escalating. There is not a simple answer on how to prevent this & not a single person who could do it alone. The only chance we have is to work together towards this as a common goal with a holistic, cross-cutting & synergistic approach.
The International Alliance therefore offers a solution by serving as an inclusive & interdisciplinary platform for stakeholders. It is a collaborative space to join forces to better understand & reduce the threat of pathogen spillover from wildlife trade & consumption, providing & communicating evidence, and supporting interventions. Thereby we reduce the risk, while improving health, equity & well-being for all species through a One Health approach.
Context
Challenges addressed
Due to the expanding of civilisation and the increase of wild animal consumption the contact between wildlife and human gets even closer and therefore the risk of pathogen spillover from wildlife trade and markets is highly increased. Both a lack of regulations and insufficient data on retail trends pose a particular challengee here.
The pace of translating information into actions is not keeping pace with the unprecedented rate of social and environmental changes that result in existential health risks from global pandemics to local family illnesses. This is because stakeholders work in siloes and knowledge remains disconnected. The International Alliance helps decision makers to take faster action and prevent pandemics directly at their source, it supports interventions from its members to better understand and reduce the threat of future spillovers, to improve health, equity, and well-being for all species.
Location
Process
Summary of the process
The International Alliance is a diverse, multi-stakeholder platform with several key components: a feature-rich website, funded projects, country packages, and a governmental facility. Members and communication management play a vital role throughout the context.
Our global community, as of February 2024, consists of 120+ national and international political, academic, and civil society organizations, along with 90+ individual scientists, experts, and academics (total of 415+ people).
The website serves as a hub to explore the Alliance's concept, showcase member support, share information with the public and community, and facilitate knowledge and experience exchange of knowledge and experiences. The Project Map and Members Area are particulary valuable tools for achieving these goals.
Working groups actively engage members in the Alliance development, leveraging the community's expert knowledge to create collective outputs.
The Alliance's offers support by—funding projects, country packages, and governmental facilities to promote best practices and address health risks coming from wildlife trade and consumption. This empowers stakeholders to develop tailored solutions for their contexts.
Building Blocks
Project Map
The Project Map serves as a tool on our website for a better visibility and visualization of projects implemented by the International Alliance member organisations: both projects funded by the Alliance and projects run independently by the Alliance's members.
As an interdisciplinary and inclusive multi-stakeholder platform bringing together different disciplines, the Alliance invites efforts on a wide range of topics related to the work and goals of the Alliance to be presented on this project map, for others to see and get connected.
Enabling factors
- willingness of member organisations to show and present their projects
- maintenance of the website
Lesson learned
In order to give the first incentive for other members to present their projects, you need an existing collection of projects to be shown at the beginning.
Resources
Funded Projects
Following two funding calls, a total of 17 projects were selected. The projects represent a very wide range of different approaches and solution ideas for pursuing the Alliance's goals, depending on the respective context.
To increase the visibility of the projects and to foster knowledge exchange they are invited to present their ongoing work, intermediate goals and preliminary results to the Alliance community through posts on the website or at online events.
Enabling factors
Sufficient funding is necessary to ensure long-term support and sustainable implementation of the project goals.
Continuous communication between those responsible for the project and the Alliance secretariat ensures the success of the project, the feedback of results to the community and thus added value for the community.
Lesson learned
Adequate feedback from project partners can be challenging and requires good communication strategies.
Resources
Country packages
The aim is to establish practices, rules and/or standards to reduce risks to the environment, human and animal health in trade in wild animals and wild animal products in selected partner countries in global biodiversity hotspot regions. Among other things, risk assessments, the design of educational measures in different formats (digital and non-digital campaigns, training courses, etc.) and the scientific monitoring of the implementation of good practices (e.g. impact assessments) are to be promoted. The Alliance brings the relevant actors together across sectors and use concrete findings to formulate adapted regulations or or supports the institutionalization of relevant practices.
Enabling factors
Existing political and GIZ structures, as well as other local partner organizations in the selected partner country.
Lesson learned
Depending on the initial situation in the partner countries, you have to start at different levels. In some cases working together at the political level is possible, in other places it is more effective to implement the goals via a partner organization that already has experience on site and a network of local actors.
Resources
Members Area
The members area is exclusive for registered members (individuals or organisations) of the Alliance. The membership is free of charge and gives you the chance to join forces for a common cause as well as connect, collaborate and partner with other members.
The Members Area serves as a platform for internal exchange, sharing of interesting articles, job opportunities and event dates as well as having access to video recordings of past events on demand.
Enabling factors
- maintaining the website and members area
- it needs motivated and committed members who are willing to actively participate on the platform
Lesson learned
At the beginning of the implementation, direct and regular contact with members is necessary to encourage them to post and interact with each other. Direct inquiries via email or reminders in the newsletter can help. Active support for posting from the secretariat is initially necessary but can be reduced over time.
Resources
Working Groups
The International Alliance currently has 3 Working Groups, which are led by the members themselves and receive support from the Alliance Secretariat. Each Working Group is led by 1-2 chairs and the group meets every 6-8 weeks to ensure a continous work process.
We currently have the following Working Groups:
- Science Policy Interface (chair: Sue Liebermann, WCS)
Considering our core understanding of wildlife we want to infuse this understanding, based on scientific evidence, into international political processes.
- Transformative System Change: The Big Picture (chair: Alex D. Greenwood, IZW Berlin; Barabara Maas, NABU)
There are underlying fundamental obstacles to achieving the Alliances objectives and goals. Identifying and addressing these is the focus of this Working Group.
- Evaluation/Effective Interventions (chair: Craig Stephen, One Health Consultant)
The aim is to gather good practices on effective interventions from Alliance members to enable learning and knowledge exchange across sectors and regions.
Enabling factors
The success of the working group depends on whether clear goals have been formulated, how committed and well- organized the chair is, how motivated the group members are and whether there is a continuous workflow.
Lesson learned
Since most members already have very demanding full-time jobs, the time capacity of individual members may change over time. It can be challenging to ensure a good workflow and working atmosphere. Appreciation and understanding are of great importance in order to enable further collaboration.
Resources
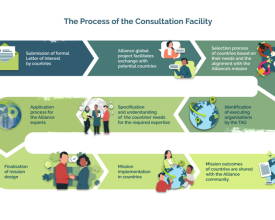
Governmental Consultation Facility
The goal of the Consultation Facility is to provide context-specific multidisciplinary consultancy services from Alliance experts to governments/governmental institutions in countries with a high risk of novel diseases of zoonotic origin to prevent spill-over infections.
The expertise of more than 180+ member organisations and individual experts in the Alliance will be used to put together those interdiscplinary teams.
The Consultation Facility specializes on medium-term, primary preventive and context-specific government advisory services with concrete results in the context of health risks in wildlife trade and consumption along the entire contact and trade chain.
Enabling factors
Effective and sustainable counseling requires thorough policy analysis/screening to identify suitable governments.
Existing political action or other political regulations regarding the intersection of wildlife and human health for example, are particulary helpful at the beginning of the consultation.
Lesson learned
The facility was launched in December 2023. For this reason, the lessons learned will only be communicated in the course of 2024.
Resources
Impacts
We have created an interdisciplinary, international, and inclusive multi-stakeholder platform with the space where different stakeholders meet, exchange, and synergize through the Newsletter, seminars, workshops, expert-talks, and working groups. To translate knowledge and science into actual change, our members work together on specific topics like the Science-Policy-Interface, Transformative System Change, or Evaluation & Effective Interventions.
We have supported the trialling of various approaches to primary pandemic prevention and currently reach over 600 people through our newsletter alone.
We develop context-specific policy recommendations, drive public awareness and therefore behavioural changes as well as fill knowledge gaps.
We work together with governments, ministries, and the public health sector through a Governmental Consultation Facility to ensure that evidence-based knowledge reaches decision-makers.
We lay the groundwork to provide stakeholders with the know-how about the health risks of wildlife trade so they can take informed action and reduce the risks of future outbreaks and pandemics.
We have placed the topic in high-level forums and helped shape international processes (CBD, CITES, Pandemic Instrument, GDG, ...). As a result, we have significantly increased the visibility of the Alliance and ensured the continuation of its work.
Beneficiaries
- Global human population, lowered risk of health and economic crises from spillover of zoonoses through pandemic prevention
- Wildlife, their health and conservation
- Environment through a better understanding of its connection to humans and animals