Preserving and improving a cultural landscape, using urban and architectural guidelines as a tool at Al Ain
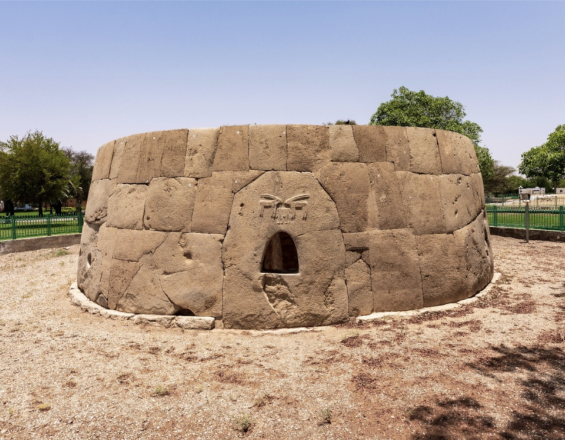

The cultural sites of Al Ain (Hafit, Hili, Bidaa Bint Saud and Oasis) were inscribed on the World Heritage List in 2011. The site is a serial property consisting of historic buildings, archaeological sites and oasian landscapes. These sites represent a culture that has evolved over time but is characterized by its ability to overcome the challenges and limitations of a natural and hostile environment and exceptional in terms of agriculture and irrigation, long-distance trade, inter-community relations, architecture and funerary traditions.
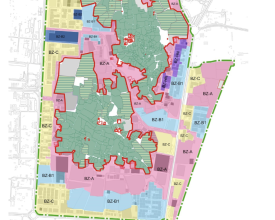
The management plan identified a variety of risks related to site complexity, including loss of context, isolation of archaeological and historical sites, urban pressure, and the risk of loss of urban and natural contexts. The project's objective was the identification and regulation of buffer zones around the cultural sites of Al Ain, which was crucial for the site's conservation in the face of building regulations and urban sprawl.
Context
Challenges addressed
Location
Impacts
The current regulation has resulted in a thorough understanding of the zones (central and buffer). It was designed to support the Department of Culture and Tourism (DCT) to protect the cultural sites of Al Ain and their buffer zones from the impact of inappropriate development and to ensure that ongoing development in these areas respects the historical setting and local character. The By-law sets out the City’s urban design guidelines for the management of current and future construction activities within and near the 17 Al Ain World Heritage sites, inside the property and at that buffer zone.
This has achieved the following objectives:
- Redefining the relationship of conservation areas with their buffer zones
- Establish a regulatory framework for the organization and control of construction activities in buffer zones
- Preserve cultural and aesthetic values and archaeological and architectural features
- Preserve the historic buildings and environment of the city, the cultural landscapes of oases and archaeological areas and parks
- Strengthening awareness of cultural heritage values
Of these initiatives, the beneficiaries include:
- Local authorities
- Local contractors
- Residents and the local community
- Owners of farms and palm groves
- Owners of heritage buildings
- Tourists
- Students
- Future generations