China Nature Watch: using technology for Biodiversity Information Collection and Application to facilitate biodiversity-friendly decision making
Biodiversity baseline data is key to conservation decision-making and practices, yet facing data deficiency and information asymmetry. With the assistance of technology tools, China Nature Watch aims at strengthening the collection of biodiversity data from various sources, especially citizen science, facilitating data applications in land use planning and public participation, and mainstreaming biodiversity conservation.
Specifically, technology brings effective solutions to 3 modules:
- Camera trap data management: developing online AI-incorporated data management system to simplify and speed up camera trap data collection and processing.
- Citizen science data visualization: using PowerBI to automatically analyze and interactively visualize species records collected by citizen scientists.
- Biodiversity Impact Assessment Tool (BiA): integrating ecological and construction data from multiple data sources to provide instant enquiry of biodiversity impact assessment for construction projects via cloud platform.
Context
Challenges addressed
Each process in biodiversity data workflow from collection, processing, visualization, to application is cumbersome and tedious that requires a lot of repetitive labor and is in urgent need of simplification and automatization.
- Camera trap data management: community-based camera trap monitoring faces bottlenecks of low efficiency (e.g., data collection from local community monitors, manual species identification) and unstable and relatively low data quality (e.g., incorrect and missing data, high rates of blank photos).
- Citizen science data visualization: visualization products are static and campaign-specific, created manually at several stages of each campaign, which cost much conservationists’ effort while only provide delayed feedbacks to citizen scientists.
- Biodiversity impact assessment: data deficiency and lack of public access to data have limited data usage scenarios. Also, biodiversity impact assessment is manually conducted for each enquiry, with reports manually composed.
Location
Process
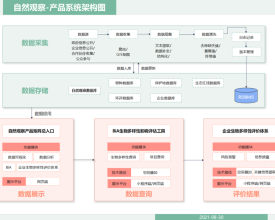
Summary of the process
The overall planning and development of supportive partnership have provided concrete foundation for the project.
Camera trap data is an integral species distribution data source for the Nature Watch database. The camera trap data management system speeds up the overall workflow and enhances the timely input of camera trap data into the database. Similar for citizen scientist data, as another species record source, the visualization platform helps inspire citizen scientists’ enthusiasm and boost species observations. Both building blocks accumulate data for the BiA tool, promoting more accurate assessment.
Moreover, the visualization platform and the BiA tool involve public communication targeted at different audience, complementing each other for the ultimate goal of biodiversity mainstreaming.
Building Blocks
Workflow analysis, Partnership building, and Overall planning
Years of research and conservation practices have not only stressed the importance of biodiversity data but also revealed the flaws of current workflow, ranging from inefficient data management, lack of data integration, to limited public-accessible data applications. Moreover, such workflow is mainly man-powered and often involves a lot of repetitive work, taking up huge amount of conservationists’ time.
Following the rapid development of technology, we have gradually realized the potential of technology to bring solutions to our “pain points” for long. In order to utilize technology tools in places in most needs, a systematic review and analysis of the current workflow was conducted to identify bottlenecks with high priorities and the possible solutions. The contemplation began in May 2018 and was materialized starting from Jun 2019 after potential technical partners emerged. Based on the systematic workflow analysis and close partnership, we made a step-by-step plan, aiming at developing modules one by one, considering our limited resource and manpower (e.g., from community-based camera trap monitoring assistant app, to BiA tool, to citizen science data visualization platform, to camera trap data management system).
Enabling factors
- A systematic review of current workflow and gap analysis that indicates where technology tools can help
- Reliable and supportive technical partners (through trial and error)
- An ambitious yet practical plan
Lesson learned
- Engaging various colleagues in the discussion of workflow and technical solutions is helpful to collect more valuable ideas.
- Different technical companies have different work styles. Choose the ones that suit your work style and values.
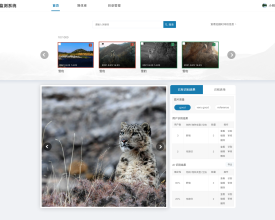
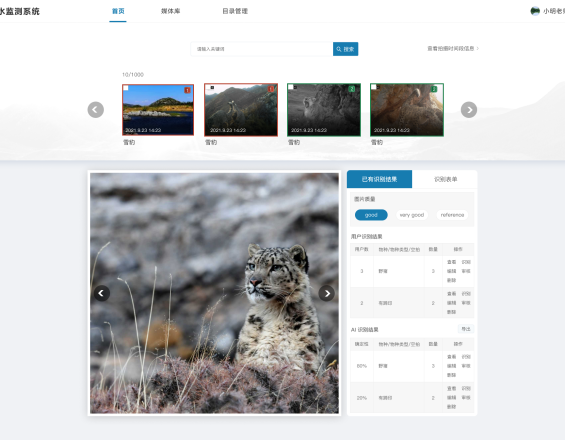
Camera trap data management system
To accelerate camera trap data workflows, an online data management system along with app-based tools and AI image recognition is being developed supported by technical partners, which consists of:
- Community-based camera trap monitoring assistant app: the app allows local monitors to automatically record the time and GPS location of camera trap setup/pickup, saving the cumbersome process of collecting data from local monitors and manual data entry. (blueprint: Jun 2019, development: Oct 2019-Feb 2020, trial and use: Mar-Oct 2020)
- AI image recognition models: AI models help detect animals and identify species in camera trap photos, which greatly reduce the number of photos that need human identification and enhance data processing efficiency.
- A series of AI models has been trained and/or tested with technical partners, including PU & PKU ResNet18 model (2018), MegaDetector (test only, 2020), MindSpore YOLOv3 model (2021).
- Online data management platform: camera trap information collected via the app along with photos are upload to a structured cloud database. The data management platform not only supports species identification via AI and human, but also enables global data search and statistics reports. (blueprint: Apr-Aug 2021, development: Sept 2021-Jun 2022, trial and use: Jul 2022)
Enabling factors
- A systematic review of the current camera trap data workflow and translating into technical system development needs
- Open-source and good-performing camera trap image AI recognition models
- Cloud resources for AI computing, data storage, etc.
- Rounds of trial use and feedback to fix bugs and improve the usability of the system
Lesson learned
- Rome was not built in a day. Due to time and resource constraints, we have to divide the system into different modules and develop modules step by step. We believe that each module itself can enhance one or more steps in our workflow and have benefited from modules before they are incorporated into the full system. Yet it is important to have a big-picture perspective in the beginning and make long-term plans for the final system integration.
- A system cannot be perfect from the start. When the app first came out and put into use in one community, it did not work as we expected and local monitors reported various types of bugs. We collected and analyzed the feedbacks to improve the UI-design and functionality of the app.
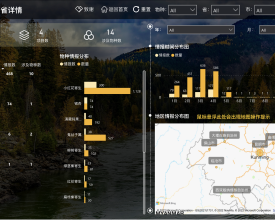
Citizen science data visualization platform
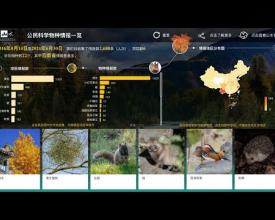
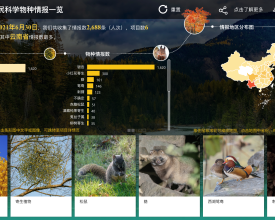
During nature watch campaigns, citizen scientists are invited to observe and record wildlife timely, which not only strengthens the connection between citizens and nature but also serves as a promising species distribution data source. Species record data collected by citizen scientists via online questionnaire automatically flows into the visualization platform database (after data cleaning and manually periodically check) and turns into intuitive and attractive visualized charts and maps (two types: spatial, spatial and temporal) via Power BI. The platform, with both web and mobile version, provides real-time feedback to citizen scientists’ nature watch efforts, boosting their sense of accomplishment and motivating their future participation in nature watch activities. Moreover, since the platform integrates multiple nature watch campaigns with links to web articles about specific analysis of each campaign, it offers a broad range of biodiversity knowledge and enables “virtual nature watch” for citizens to get to know wildlife in other regions.
A brief timeline of the platform:
- Jan-Feb 2021: form team, analyze analysis, make blueprint
- Mar-Jun 2021: develop database and platform
- Jul-Aug 2021: trial test
- Sept 2021: go live and promotion
Enabling factors
- A well-designed data-collection questionnaire and automatic data cleaning mechanism to ensure data quality and a manually periodically check (normally once a season) to ensure data reality.
- Visualization methods selection and aesthetic design with the engagement of citizen scientists.
- PowerBI technology.
- Citizen scientist WeChat community operation and maintenance.
Lesson learned
- As a public outreach product, it would never be too much for polishing contents and aesthetic design to make the platform user-friendly and attractive.
- Engaging users in the planning stage and collecting their thoughts is very helpful for identifying user needs.
- Questionnaires are needed to be well-designed and citizen scientists are needed to be well-trained before recording data. Otherwise, it’s easy to cause data loss.
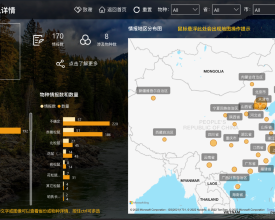
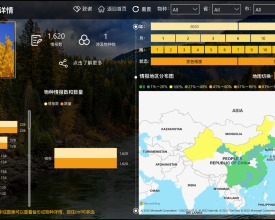
Biodiversity Impact Assessment Tool (BiA)
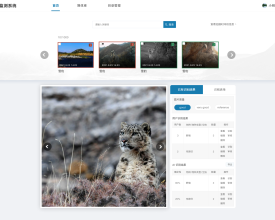
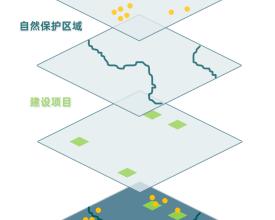
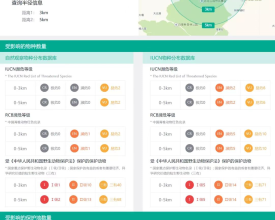
To enable automatic and instant biodiversity impact assessment enquiry, the BiA tool has been developed to facilitate enquiry services for land planners and other interested parties via Azure platform. The BiA tool works by overlaying the enquiry site or region (or existing construction projects) with multiple geographic layers including species distribution and protected area range to investigate if the site or region is within certain distance (e.g., 3 km, 5 km) from and may cause impact on endangered species habitat and/or protected areas. The assessment reports illustrate ecological and environmental risks of construction projects for decision-makers and could hopefully promotes them to take biodiversity into consideration.
A brief timeline of the BiA tool:
- Apr-Jun 2020: team formation, requirement communication, system development plan
- Jul-Sept 2020: tool development
- Oct 2020: trial test, application and dissemination
- (in preparation) Apr-Sept 2022: system upgrade
Enabling factors
- Years of data collection accumulation and constant thinking of data application approaches.
- Theoretical & technical basis accumulated from long-term research and conservation practice.
- Promotion of the BiA tool to its potential users, like governments, investors, and enterprise.
- Keeping track of tool operation and user feedback to devise further upgrade of the tool.
Lesson learned
- Data application is the foremost step in the whole data workflow, where the data turns into valuable information for stakeholders. Effective data application reports should bear the audience in mind (e.g., being concise and focused).
- The complete of development and releasing is not the last step for a tool. Finding potential users and persuading them to use the tool is also very important. A tool has to be used to provide the most value.
Impacts
Technology solutions have optimized biodiversity data workflow and promoted data applications:
- Camera trap data management: The community-based camera trap monitoring assistant app has made data recording easier for 86 local community monitors in charge of camera trap setup/pickup in field. AI image recognition models have processed over 380,000 camera trap images, substituting more than 100 hours of labor. Such acceleration in data collection and processing enables timely feedback to stakeholders and supports conservation decision-making.
- Citizen science data visualization: Through visualizing 2688 records of 22 species collected during six campaigns in 2016-2021 and automatically updating newly collected records, the platform has provided spatial, temporal, and interactive feedbacks to citizen scientist participants and significantly boosted interests in nature watch activities.
- BiA tool: The Nature Watch database maintains biodiversity baseline data collected from multiple data sources including species records (2591 species, 1.35 million records) and protected areas (6 national parks, 474 national protected areas, etc.). Up till now, the BiA tool has provided interactive and visualized biodiversity impact assessment enquiry services to more than 1260 construction project planners and other stakeholders, facilitating biodiversity-friendly decision making.
Beneficiaries
- Conservationists: enhanced efficiency
- Local communities: enhanced efficiency and timely feedback
- Citizen scientists: timely feedback
- Government agencies, academic institution, public: easy access to biodiversity data