Acoustic Monitoring for Improving the Conservation of Critically Endangered Hainan Gibbon
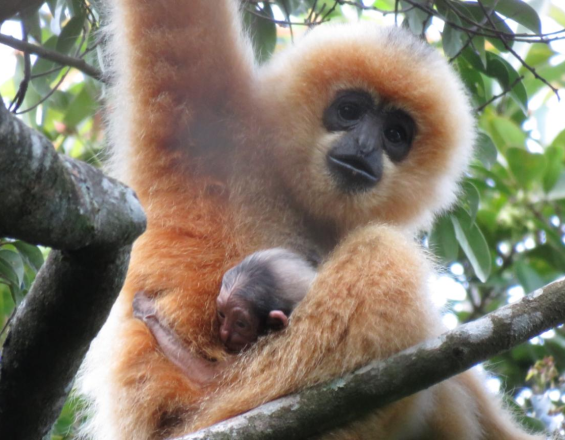

The Hainan gibbon (Nomascus hainanus) is one of the most endangered primates in the world, living in the Bawangling area of Hainan Province, China. Comprehensive tracking and monitoring is required for better conservation, but because of the difficulty in vivo tracking, acoustic equipment is needed for monitoring.
“Tech4Nature” is a global project jointly launched by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) and Huawei, aiming to develop more scientific protection measures, combined with the ICT industry, digital technology and IUCN Green List standards, provides technical support for the acoustic monitoring project of Hainan gibbons. To date, full coverage of 5 family groups monitoring has been achieved, automatic identification and real-time back transmission of Hainan gibbon acoustic monitoring have been realized.
Context
Challenges addressed
- Hainan Gibbon monitoring
- biodiversity loss
- Relationship between human and nature
Location
Process
Summary of the process
The three building blocks are carried out in chronological order. Field Research (BB1) is the basis for Sound Recording Equipment layout and installation (BB2) and so as BB2 for Data Quantification and Database Establishment (BB3), Sound Pattern Analysis (BB4), and Recognition Modelling(BB5). The above outputs has been exchanged and conmmunicated during International Symposium (BB6) for furthur impacts. The three blocks share a common goal of acoustic monitoring and individual recognition of Hainan Gibbons. They are designed to allow for step-by-step data collection, storage and analysis to achieve the above-mentioned objectives.
Building Blocks
Field Research
From late November 2021 to early December 2021, the Hainan Institute of National Park (HINP) conducted field research in and around the five family groups (group A - E) of gibbons in the reserve with the participation of relevant experts and staff from the Bawangling Reserve. The research has set up 8 stationed sites and 21 surveillance sites, covering the habitat of each Hainan gibbon population, with 48 team members participating simultaneously.
Enabling factors
- Past data accumulation of Hainan gibbons monitoring
- Participation of experienced experts
- Support from the Hainan Institute of National Park (HINP)
Lesson learned
The field research has provided data support for the protection of Hainan gibbons, and played a key role in timely grasping information and formulating conservation plans.
Sound Recording Equipment layout and installation
Based on the research results, combined with the coverage of 4G signal, a set of domestic automatic sound recording equipment with 4G signal, which has a real-time transmission function (product model: LBird-01211) was installed in the typical environment of Hainan gibbons in the Bawangling Reserve.
Enabling factors
The field research results showed that group C and group E have strong 4G signal coverage, which can meet the remote transmission conditions for recording equipment as tested by technicians. Therefore, three and two sets of equipment were chosen to be deployed in group C and group E respectively.
Lesson learned
The equipment analyzes the remotely acquired sound data including the environment and location information and tries to practice individual vocal recognition in the layout area from the perspective of sounding.
Data Quantification and Database Establishment
Import the raw data of sound into Adobe Audition 3.0 or Avisoft-SASLab Pro sound analysis software, resampled (Sample size: 44100 Hz; Window size: 1024 points), and then saved separately in WAV format. High-quality waveforms and sonograms were selected to measure characteristics of Hainan gibbons’ calls, to analyze the differences in acoustic indexes between individuals, and to build a database of Hainan gibbon sound patterns on an individual basis. Then, perform individual sound recognition using the implemented sound recognition model. Finally, the effectiveness of the sound acquisition is evaluated, and the accuracy of the sound recognition is assessed. Among them, the evaluation of the sound recognition effect is done mainly by comparing with the field research and other sound monitoring results.
Enabling factors
Based on the acquired time-frequency domain characteristics of Hainan gibbons, the parameters used for automatic recognition were determined in conjunction with the vocal database. The selected time-frequency parameters were imported into the automatic recognition software and the developed algorithm program to automatically identify and extract Hainan gibbon calls from the recordings. Information such as the number of gibbons that may be present in the sound data is evaluated by different clustering and discriminative methods.
Lesson learned
The fully-automated acoustic monitoring equipment is of vital use for data processing in this project. The transmitted sound data is automatically stored in Huawei cloud space. Once the Hainan biodiversity sound pattern Huawei cloud database be established, individual sound recognition could be realized.
Sound pattern analysis
The manual screening of 532 Hainan gibbon acoustic sample has been completed, including those obtained during tracking and observation of gibbons using a portable recorder and those obtained using an automated recorder. During the screening process, three recording qualities were initially categorized, namely hight, medium, and low. 44 high-quality recordings from seven individual callers were obtained. The seven individual callers were GAM1、GBM1、GBSA、GCM1、GCM2、GDM1、GEM1, where the letter after “G” represents the family group number and the letter after “M/S” represents the individual number of adult male/subadult male individual number. Only about 40.9% of the recordings were made manually. The raw files of all automated recordings were provided by the team of professor Wang Jichao, and the related data were backed up at Hainan Institute of National Park.
Enabling factors
Mel-frequency cepstrum coefficients (MFCCs) is a method of extracting frequency envelope features by cepstrum after weakening the high-frenquency information on the basis of human hearing[1], which has a wide range of applications in the field of human and bioacoustics. In this study, MFCCs and the first-order and second-order differences (△、△2) are used to achieve automated feature extraction.
Lesson learned
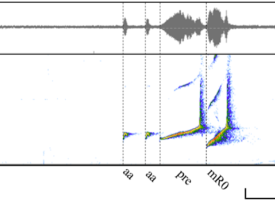
5 signature notes of the male Hainan gibbon have been identified (Fig.1), including boom note, aa note, pre-modulated note, modulated-R0 note, and modulated-R1 note.
According to the acoustic niche hypothesis, the calls of different species are differentiated in the time and frequency domains (see Fig. 2), so extracting features in a specific frequency range can greatly reduce the influence of noise, and the smaller the frequency range delineated, the more likely it is that more noise will be excluded. In addition, when the structure of each minimum recognition units (MRUs) is the same, the difficulty of recognition is greatly reduced.
In view of the above situation, in this phase of the research, we tried (1) applying pre only and (2) using pre + n×mR0 as MRU, respectively, and comparing the classification results so as to determine the most appropriate feature extraction in the subsequent work. In the case of voice annotation, all the above steps can be implemented automatically by R language code.
Recognition Modelling
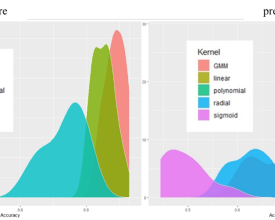
Due to the excessive number of features, a 10-fold cross-validated SVM-RFE was used to rank the importance of the features after extracting them, and then the features were added sequentially for LDA classification to record the change in accurancy with the number of features selected, and finally the best number of features was recorded as the input for the subsequent classifications (see Fig. 8). The highest accurancy for LDA classification was 89.2% (pre) / 95.6% (pre + n×mR0).
Since none of the MFCCs extracted with a fixed number of windows achieved better results than the GMM fitting method for LDA classification (6-window: 86.6%; 10-window: 88.5%; 100-window: <80%), we tested the effectiveness of the other classifiers using only the features extracted by the GMM fitting method. In this test, we randomly selected 20% of the data as the test set, and the rest of the data were used to train the classifier, which were repeated 10 times for each kernel function to record the distribution of the accuracy. Among them, the classification effect of GMM is poor when using only pre as MRU, while the effect is generally better than using only pre when using pre + n×mR0 as MRU.
Enabling factors
There are many classifiers that ca be used for individual recognition. Considering the performances and possibilities of the classifiers, this research compared the classification effectiveness of three classifiers that have been developed considerably in the field of gibbon bioacoustics or human sound pattern recognition, i.e., (1) linear discriminant analysis (LDA), (2) support vector machine (SVM) and (3) GMM (classification by determining the similarity between the data to be measured and the existing data).
Lesson learned
The basic method of sound pattern characteristics extraction has been identified, and a preliminary system method for individual sound recognition of Hainan gibbons has been established. Our preliminary results show that the existing system method is relatively reliable, and is to achieve the expected goals of the project. Among them, using pre + n×mR0 as MRU, extracting sound pattern characteristics using GMM fitting method, and using linear SVM for classification would be more effective. In the follow-up work, the data of rare individuals will be constantly supplemented, and design of the algorithm system will be improved, the ability of the classifier to recognise unknown individuals will be given, and the performance of the system will be comprehensively evaluated, so as to ultimately realise the recognition of individual sound of Hainan gibbons.
International Symposium
The symposium was guided by Foreign Affairs Office of Hainan Province, Department of Natural Resources and Planning of Hainan Province, Department of Ecology and Environment of Hainan Province, Forestry Department of Hainan Province; and supported by the big data lab of Research Institute for Eco-civilization, CASS, the research think tank of Research Institute for Eco-civilization, CASS, Institute of Zoology Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Garden Chinese Academy of Sciences, Institute for Carbon Neutrality, Tsinghua University, Advanced Interdisciplinary Institute of Environment and Ecology, Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., Hainan University, Hainan Normal University, Federation of Hainan Academicians, the Sanya Research Base of the Internation Centre for Bamboo and Rattan.
The two-day symposium focused on the theme of “conservation of the flagship species of tropical rainforests-gibbons” “conservation of tropical rainforests’biodiversity, and was held in a combination of online and offline activities.
Enabling factors
On the occasion of the third anniversary of the establishment of the Hainan Institute of National Park and the 8th international gibbon day (24th October, 2022), the Forestry Department of Hainan Province, Wuzhishan municipai government, Hainan green island tropical rainforest public welfare foundation, and Hainan Institute of National Park co-sponsored the “2022 tropical rainforest international conservation symposium” themed “protecting tropical rainforest·realizing ecological values”, which was supported by Eco Foundation Global (EFG).
Lesson learned
The Conference reached the following concrete results:
- Signing of the GGN Charter (Global Gibbon Conservation Network Charter).
- l Announcement of the establishment of the first GGN Secretariat at the Hainan Institute of National Park, and the global launch of the GGN Logo.
- This is the first of China’s first five national parks, the first domestic conservation research organisations initiated the establishment of international organisations for the protection of cherished species protection, which is of historical significance.
- Publish the Global Gibbon Network the declaration of conservation in the form of GGN joining hands with IUCN SSA, with the gibbon as the representative.
- Introducing the List of Priority Species for Conservation in Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park with the case of KBAs, and officially releasing the List of Priority Species for Conservation in Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park.
Impacts
- Enhance monitoring efficiency: The equipment installed in this project can be activated by the sound of Hainan gibbons, then records the data and transmits back in real time, and can also realize automatic sound recognition, which effectively improves the efficiency of monitoring, and achieves a new stage in Hainan gibbon acoustic monitoring.
- Assist in biodiversity conservation: The establishment of the cloud database will provide a scientific basis for the discovery of potential solitary or groups of Hainan gibbon, contributing to the biodiversity conservation in Hainan.
- Contribute to the study of human: Hainan gibbons have a complex acoustic communication system similar to humans, and a stable monogamous or bi-marital mate system. The study of their behaviors starting from their acoustic can help us better understand the origins of human society, family, language, communication, and the evolution of other behaviors.
- Increase the conservation awareness: The exchange experience of applying technologies in Hainan gibbon conservation, based on the indication and reference value of scientific means such as sound recognition and precise monitoring in the stable long-term development of Hainan gibbons.
Beneficiaries
- Hainan gibbons
- Local communities
- Protected areas communities
- Academia
- Visitors
Sustainable Development Goals
Story
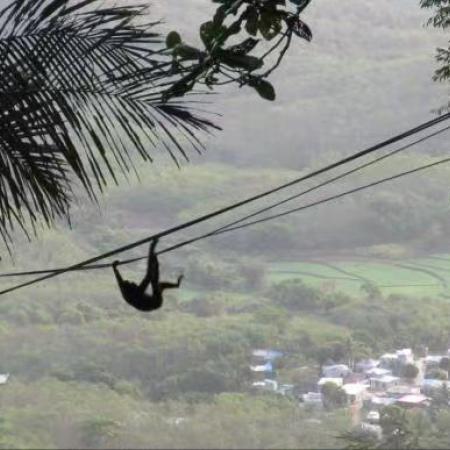

In the past, when monitoring Hainan gibbons, our team members used to chase after them in the mountains, carrying cameras, GPS devices, and other equipment. But now, we employ technology for smart monitoring of Hainan gibbons. For example, we install infrared cameras, accoustic monitoring and real-time monitoring equipment within the habitat of the Hainan gibbons. This way, we no longer have to worry about physical endurance and weather conditions. The combination of human presence and technology effectively addresses issues such as working in adverse weather conditions and monitoring during nighttime when humans need rest. When typhoon hit Hainan, causing landslides that obstructed many of the Hainan gibbons' activity routes among the mountains. To better monitor their activity routes, we set up a rope corridor in the valleys affected by landslides. Near this rope corridor, we monitored and observed the Hainan gibbons. We wondered if they would utilize the rope corridor we had constructed. After approximately two months, we were delighted to see the first images captured by the infrared cameras showing gibbons using the rope corridor to access the opposite habitat. This made us feel that our efforts were truly worthwhile. Hainan gibbons are highly intelligent creatures.