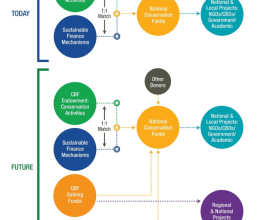
A regional sustainable financing architecture for conservation

The Caribbean Biodiversity Fund (CBF) is the realization of the vision to create reliable, long-term funding for conservation and sustainable development in the Caribbean. The CBF and its National Conservation Trust Funds form the regional sustainable finance architecture, which support and incentives Caribbean nations to meet the goals under the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), the Caribbean Challenge Initiative, and other international and regional commitments. The CBF is a umbrella fund with permanent (an endowment fund) and non-permanent funding (sinking fund).
Context
Challenges addressed
- Limited resources for conservation in the Caribbean. The CBF and the Regional Sustainable Financing Architecture for Conservation is a new and sustainable source of funding to address environmental challenges.
- Environment is low in the regional political priorities. The CBF and the NCTFs will be crucial in raising the profile of environment and conservation in the region.
Location
Process
Summary of the process
The building blocks describe 5 key areas in the design, establishment, current and future implementation, and monitoring and evaluation of this solution. While there are some sequential aspects around these building blocks, their implementation has and is often occurring in a parallel manner. For example, the CBF has been established first and now most of the national conservation trust funds are being established. The operationalization of the different trust funds will also not occur at the same time. Meanwhile maintaining the governments‘ and partners’ commitment is an important factor throughout all the building blocks.
Building Blocks
Government commitment
Governments are key in the success of the regional collaboration. Their political commitment to the Caribbean Challenge Initiative (CCI) Goals has been essential to attract donors to help achieve these goals, including building the finance architecture. Governments participate as observers and/or focal points in regional trust fund board meetings and are also part of the National Conservation Trust Funds (NCTF) boards.
Enabling factors
- Open, transparent and direct dialogue with governments.
- Identifiable benefits for advancing national and regional conservation priorities.
- Donor’s and partners’ commitments to provide funds and other technical assistance.
Lesson learned
- Building political commitment is a lengthy process that requires technical and policy inputs at multiple levels in government from technical staff, to middle/senior management positions and the highest levels ministers/heads of governments.
- Donor’s commitment provides countries with additional security and confidence with regards to their political commitment and knowing that partners are ready to assist.
Independent National Conservation Trust Funds (NCTFs)
CBF endowment proceeds will be channeled through the NCTFs, which in turn will lead the grant-making process for on the ground and water activities. They are governed by majority non-government member boards reflecting a broad range of sectors and interests, and provide grants to both government and civil society.
Drawing on internationally recognized standards, the characteristics of NCTFs to be supported by the CBF are:
- Purpose: Purpose aligned with the purpose of the CBF.
- Board composition: Broad composition and representation, with majority civil society board membership and no single majority interest group dominating the board.
- Civil society board members: Board members representing civil society not solely selected by the government.
- Asset control: Well-designed and independent asset control.
- Audit requirements: Well-defined annual external audit requirements.
- Grants: Grant making to government and civil society.
Enabling factors
- Multiple-stakeholder dialogue to guarantee participation of all relevant sectors in governance structures.
- Clear legal instruments that reflect independent structures and guarantee the rights and responsibilities of the different stakeholders.
Lesson learned
- It is challenging to find the right balance between government and civil society representation in governance structures at the national level. Government actors may feel that majority non-governmental governance structure will exclude them from decision making and civil society may feel that majority government boards will result in inefficient institutions controlled by government.
- Donors have a strong preference for NCTFs governance that is independent from government control, although government may participate in it.
- Finding a balance in NCTFs constitutive instruments and other agreements to different points of views, needs and requirements, and reassure all stakeholders that the governance structure and decision making process will be transparent and inclusive is essential.
Successful trust fund operationalization
Skilled personnel, effective governance and functioning technical systems are essential for successful operation. Key elements to support this include training for National Conservation Trust Funds, staff and board members, establishment of clear accounting systems, operations manuals, learning from best practices, mentoring, and peer exchange.
In this regard, the CBF has established training on its accounting system for its staff. It has also become a member of the Latin American and Caribbean Network of Conservation Trust Funds (RedLAC) to learn from similar institutions.
Enabling factors
- Staffing: Hiring of a highly capable executive director. Additional support staff may also be needed.
- Office: Set up initial logistical office operations.
- Board: Establishment and training of the board of directors and executive director.
- Committees: Establishment of board sub-committees and other advisory committees.
- Development of an operations manual.
- Finance and accounting.
- Mentoring and overall organizational development.
Lesson learned
- Developing all necessary systems (accounting, other operations systems) often takes longer than expected. It is important to establish realistic timelines for establishing a CTFs operation. Tasks for the appropriate set-up of operations multiply quickly.
- Support from donors and partners; not only in cash, but also in-kind, is key during the initial 1-2 years of operations.
- Mistakes along the way will occur and it is important to recognize and address these quickly and continue to move forward.
- It is key essential to have formal and informal advisor and other kinds of technical support. Many other CTF are currently under operation and can provide important insights in this process. RedLAC is a key resource for example.
Strategic plan and fundraising strategy
Developed and implemented jointly with donors, countries and partners, the strong strategic plan includes:
- Consolidating the establishment of the fund's architecture
- Opening new thematic windows and attracting new countries to be part of the architecture
- Establishing a fundraising strategy
- Establishing a marketing and communications plan
- Establishing a monitoring and evaluation system
Enabling factors
- Consultations: A thorough consultation process will allow to develop a strong strategic plan for the CBF.
- Measurable objectives and indicators: The Plan needs to include measurable objectives and indicators in order to assess its effectiveness.
Lesson learned
- It is crucial for the strategic plan to be an inclusive document with ample participation from all stakeholders
Common trust fund monitoring
Two compatible monitoring systems being built track financial resources and conservation impact across regional and national trust funds. Combined, these systems establish a robust M&E framework to measure for impact, organizational learning and donor reporting, using applicable regional indicators.
Enabling factors
- Development of region wide applicable reporting and indicators: Many sources of information and elements for these indicators are already available within and outside the region and would not need to be created in a vacuum.
Lesson learned
- Learn from experiences of similar institutions to establish the appropriate monitoring and evaluation system parameters
Impacts
As a regional conservation trust fund, the CBF is a new source of funding in the Caribbean. Thus far, nine National Conservation Trust Funds (NCTFs) are legally established and at different stages of becoming fully operational, with additional countries interested in joining the process. Moreover, all NCTFs have identified and are pursuing additional sustainable financial mechanism to finance biodiversity management activities. With three NCTFs official agreements with CBF have been signed and payments will start flowing in the coming months. Once the architecture is fully functional the CBF, through its endowment, expects to generate approximately US$1.5 – 1.8million/year to be channeled through the NCTFs. New sustainable finance mechanisms established by the NCTFs would match this amount. In addition, a new US$26.5 million sinking fund focused on ecosystem-based adaptation is expected to significantly contribute to create adaptation solutions for Caribbean islands.
Beneficiaries
- The National Conservation Trust Funds
- Civil society
- Government institutions
- Community-based organizations
Sustainable Development Goals
Story
tba