Identification of forest landscape restoration options at subnational level
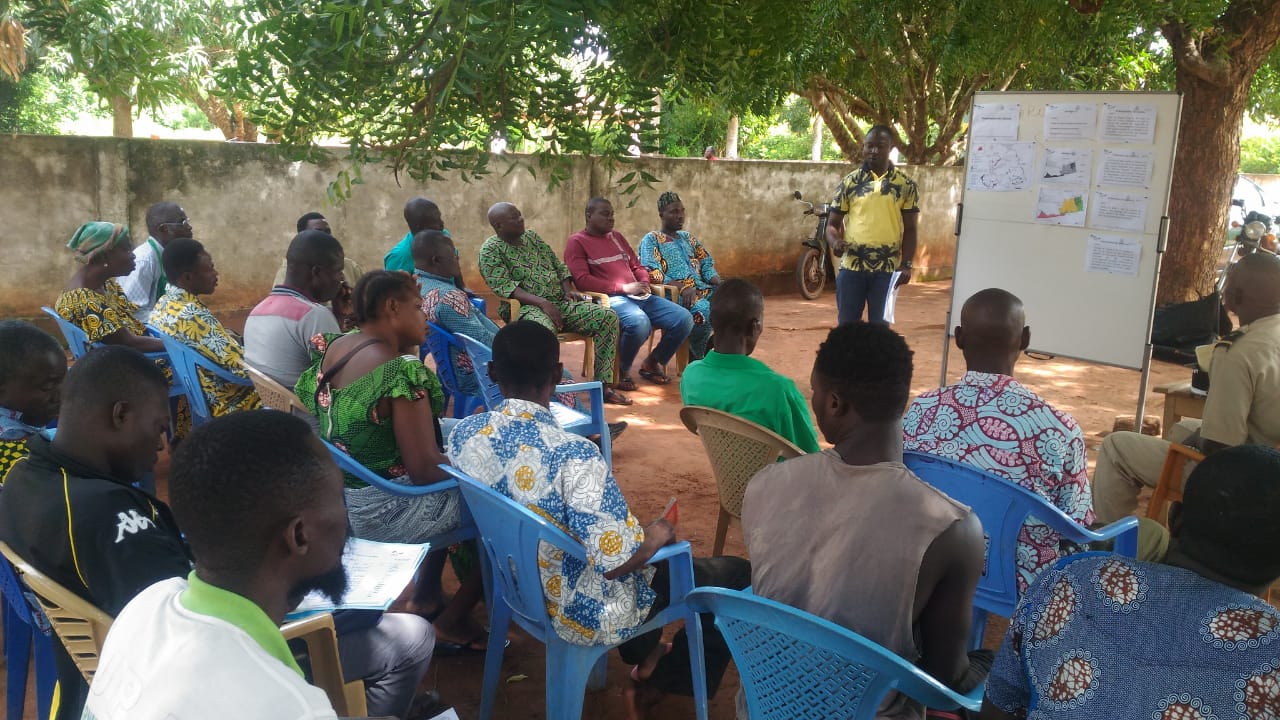
Consultation and discussion about restoration options
GIZ/ProREDD
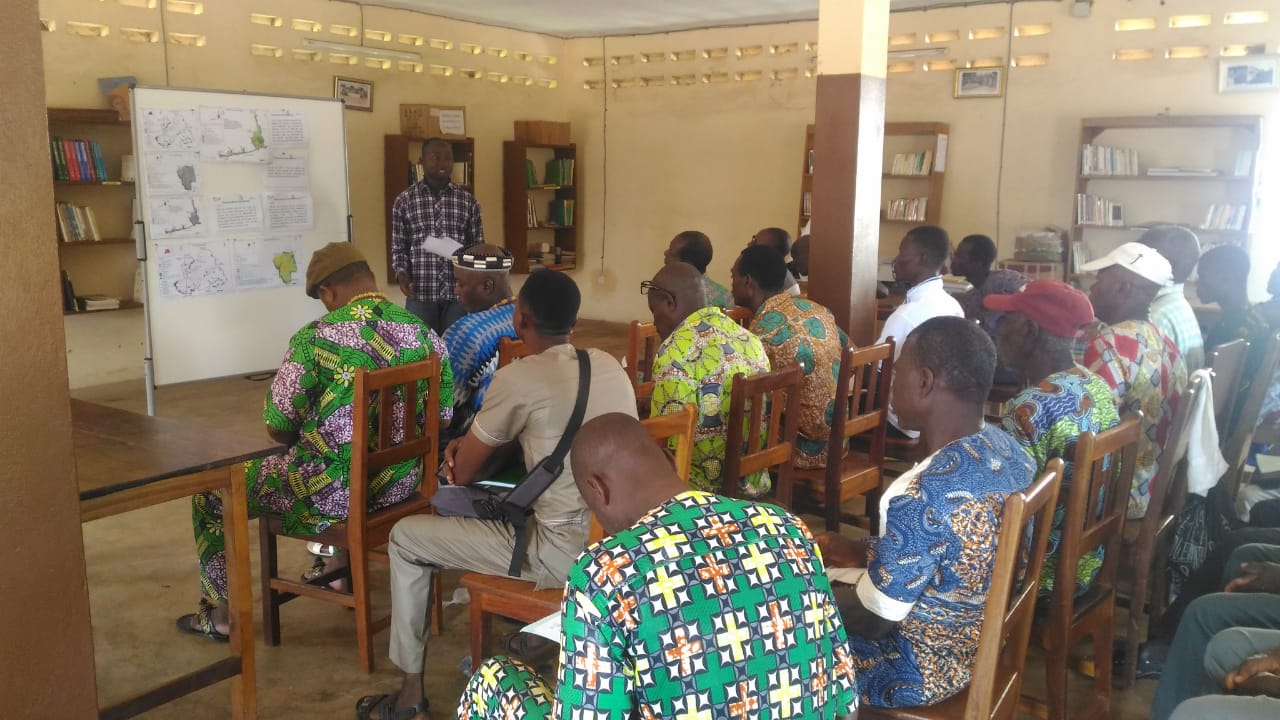
Consultation and discussion about restoration options in Aklakou canton
GIZ/ProREDD
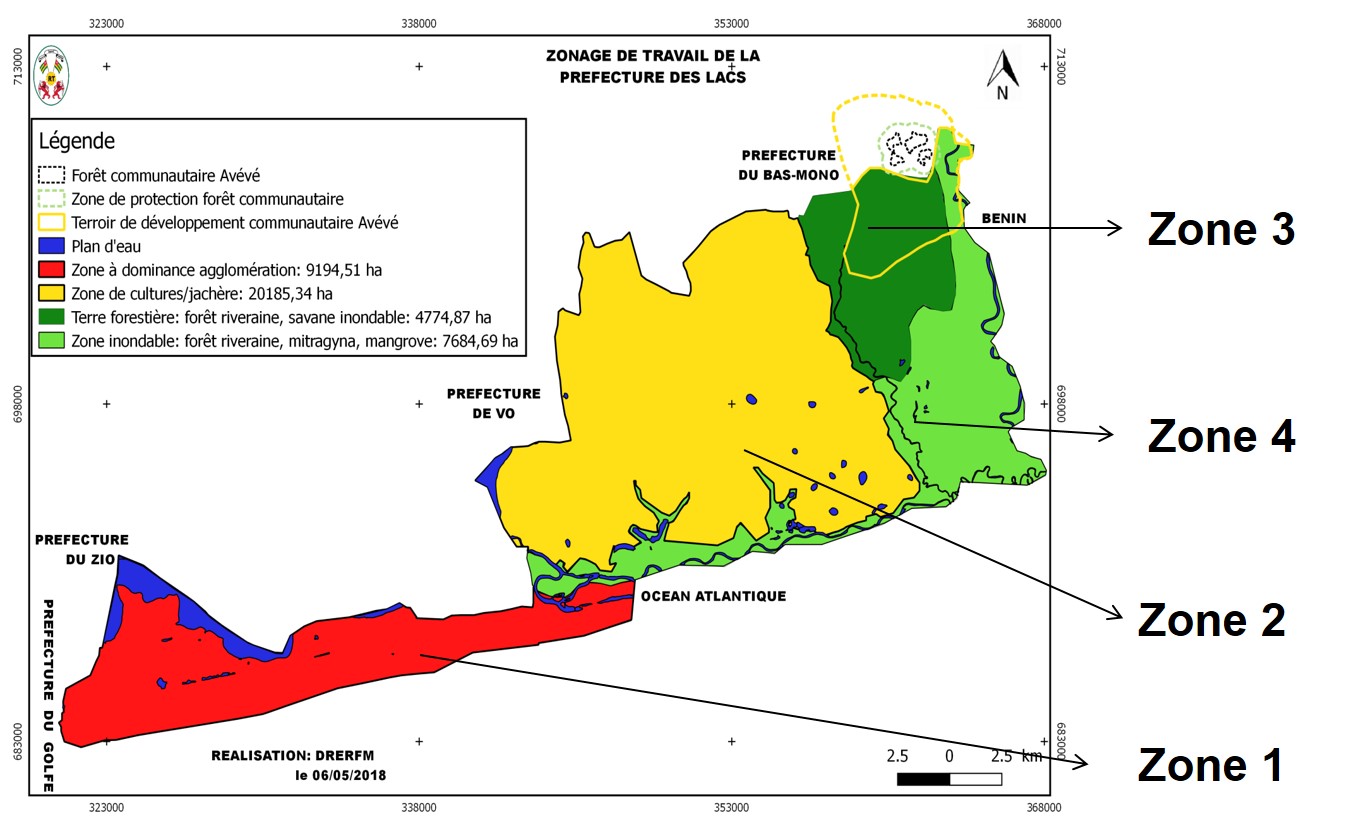
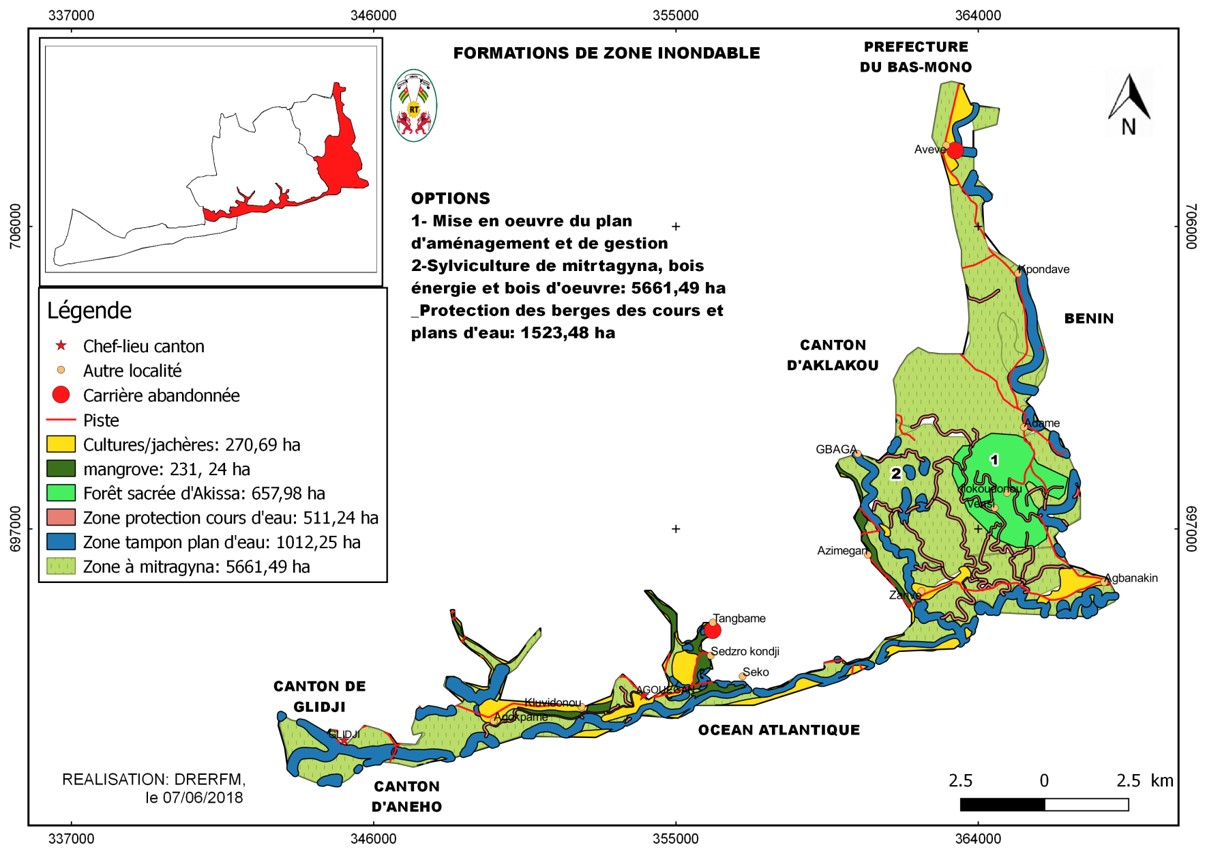
Zones for forest landscape restoration activities
GIZ/ProREDD
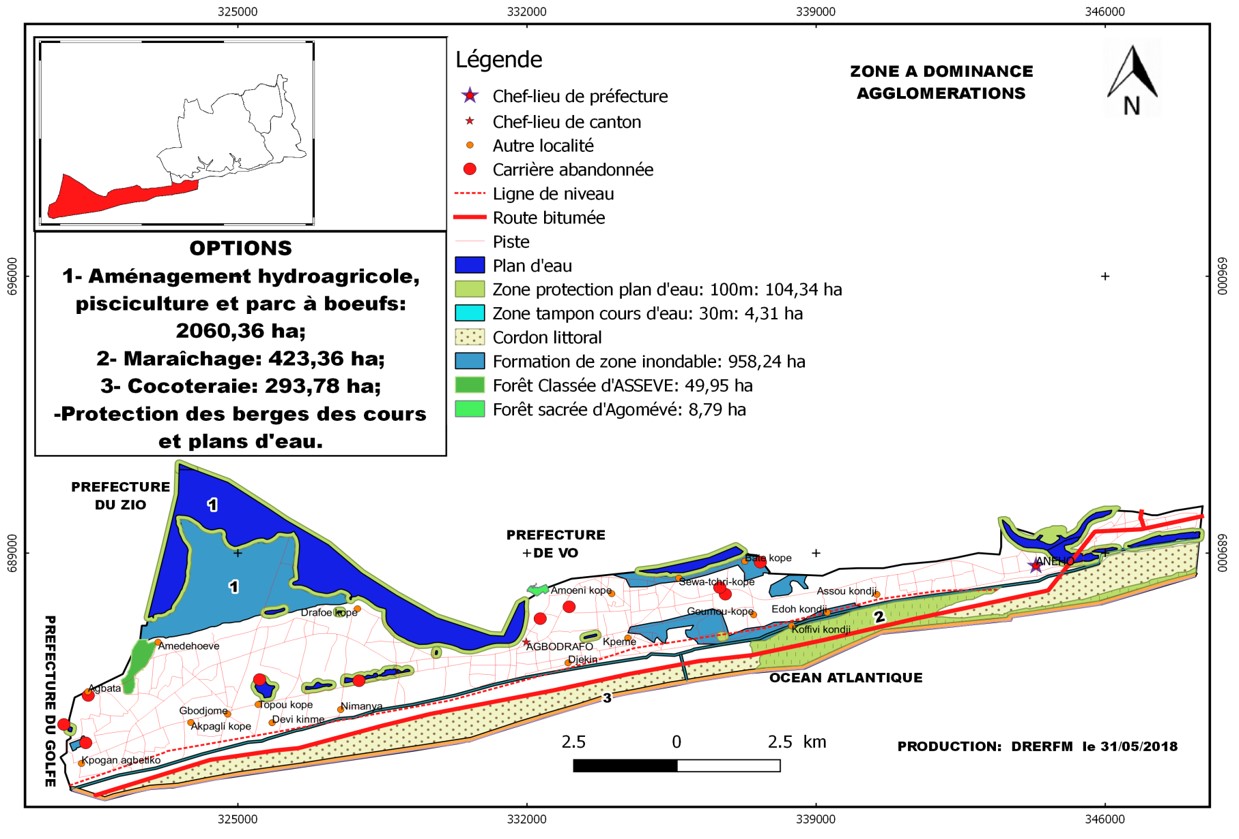
Zone 1 - Densely populated land (forest land, farmland, settlements): forest enrichment, agroforestry, river bank restoration)
GIZ/ProREDD
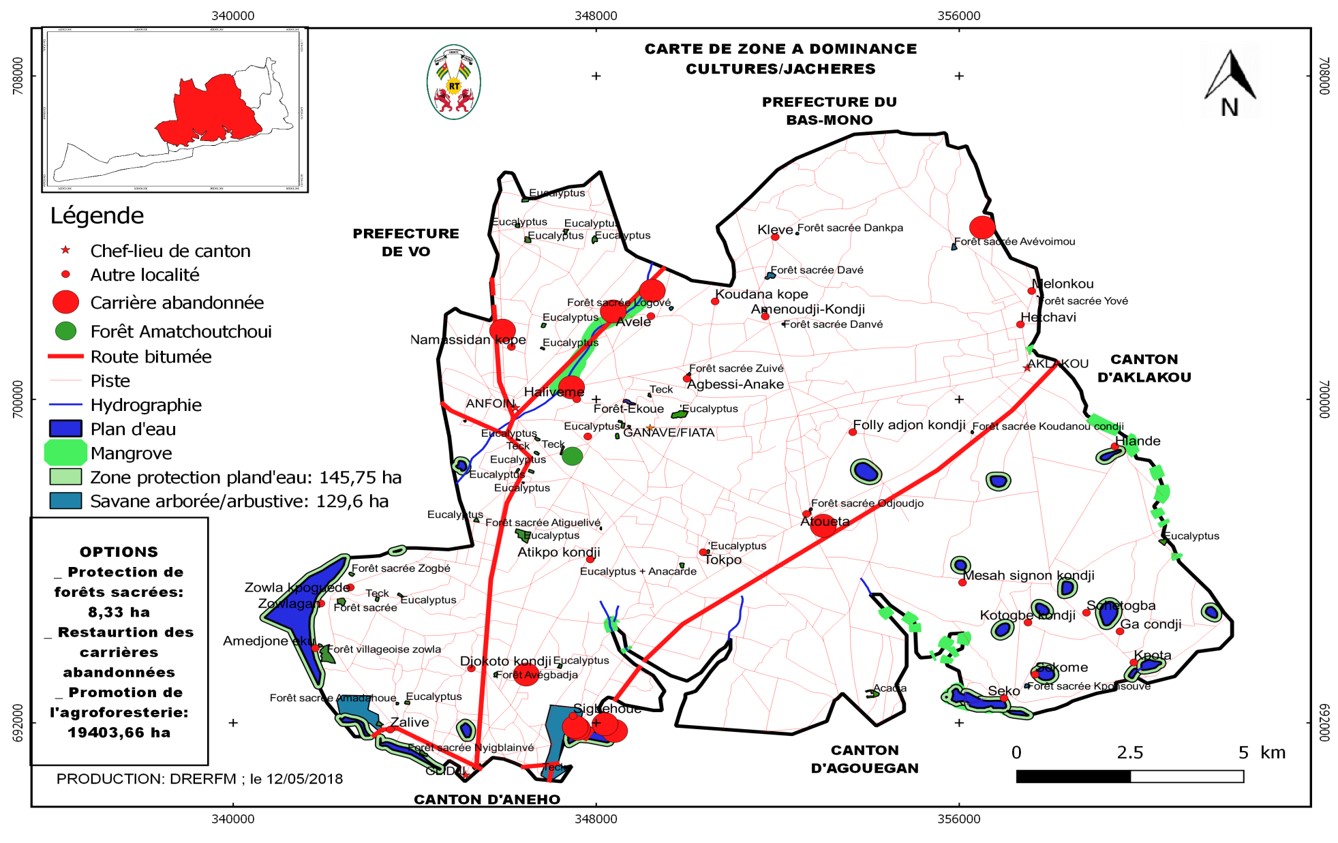
Zone 2 - Agricultural land: improved community forest management, enrichment of agroforestry systems, buffer zones around water bodies, wood energy forests
GIZ/ProREDD
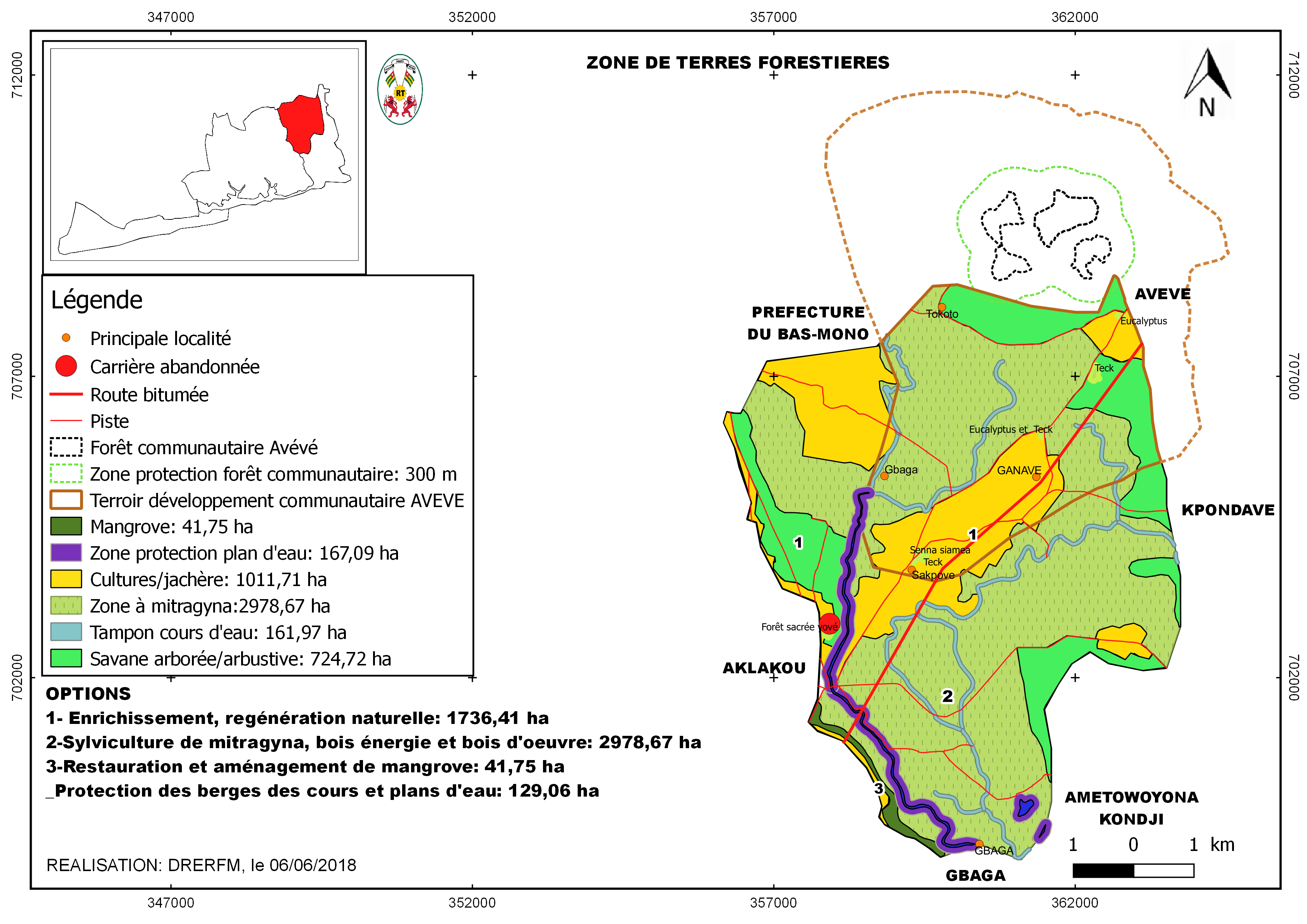
Zone 3 - 3. Dense forest, shrubland, riparian forests & savannahs: restoration of swampy savanna, riverbanks & community forests, fallow enrichment, improved pasture management
GIZ/ProREDD
Zone 4 - 4. Wetlands, marshes, mangroves, grasslands: wetland & mangrove restoration
GIZ/ProREDD
Results of the participatory mapping and forest inventory allowed to assess forest resources and identify concrete priority options for landscape restoration in 4 zones.
Criteria for selecting priority options:
- promote the restoration of natural forests, fragile and specific ecosystems,
- achieve societal goals and objectives related to the conservation of biodiversity and human well-being,
- to be implemented in the framework of existing projects in different land tenure types (protected areas, community or village forests, sacred sites),
- limiting the fragmentation of forest areas and maintaining the connection of natural habitats.
Restoration options include the following:
- Densely populated land (forest land, farmland, settlements): forest enrichment, agroforestry, river bank restoration)
- Agricultural land: improved community forest management, enrichment of agroforestry systems, buffer zones around water bodies, wood energy forests
- Dense forest, shrubland, riparian forests & savannahs: restoration of swampy savanna, riverbanks & community forests, fallow enrichment, improved pasture management
- Wetlands, marshes, mangroves, grasslands: wetland & mangrove restoration
- National strategy for the conservation, restoration and sustainable management of mangroves
- Forestry Master Plan of the Maritime Region
- National REDD+ strategy is under development
- National restoration option assessment methodology (ROAM)
- Community knowledge of resources
- A good collaboration between national, regional and prefectural government and CSO representatives.
- Prioritization was highly participatory involving communities of all 9 cantons, civil society organizations, agricultural extension services and local, regional and national forest administrations
- Valuing the knowledge of local communities in the process is extremely important and was not done intensively in the past
- Consideration and respect of the ancestral practices of the communities is key and have to be taking into account; access to sacred forests was only possible by adhering to customary and traditional procedures
- Knowledge of local languages, traditions and procedures was a key element of success
- Understanding and close coordination with local authorities was another factor of success