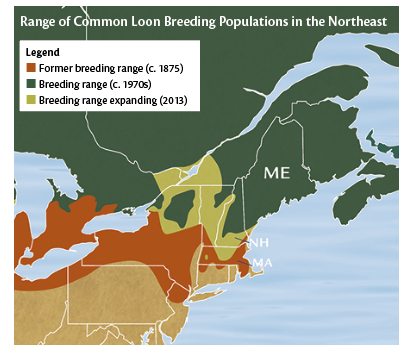

In 1974, New Hampshire marked the southern edge of the range for Common Loons, and at the time that range was retracting. Recovery efforts carried out by loon conservation groups in New Hampshire and Vermont helped restore loon populations in those states.
In Massachusetts, extirpation has made recovery in that state much slower. Currently, loon recovery in Massachusetts is still dependent on breeding success in northern New England and New York. BRI’s translocation research being carried out in Massachusetts provides an example of how a population at the edge of its range can be restored.
Working with state and local agencies as well as lake landowners helped facilitate the process of identifying restoration sites and source populations.
Initial planning is critical to success.