Participatory mapping at community level
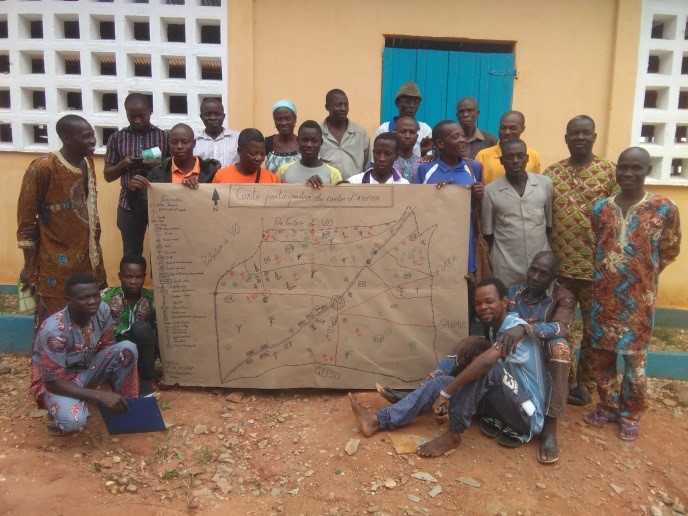
Result of participatory mapping
GIZ/ProREDD
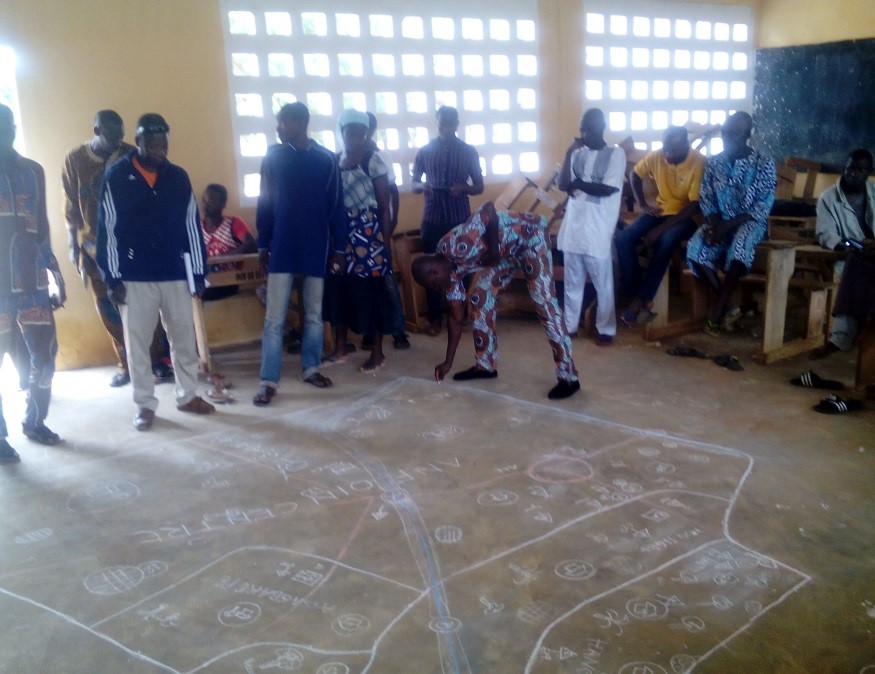
Elaboration des cartes participatives
GIZ/ProREDD
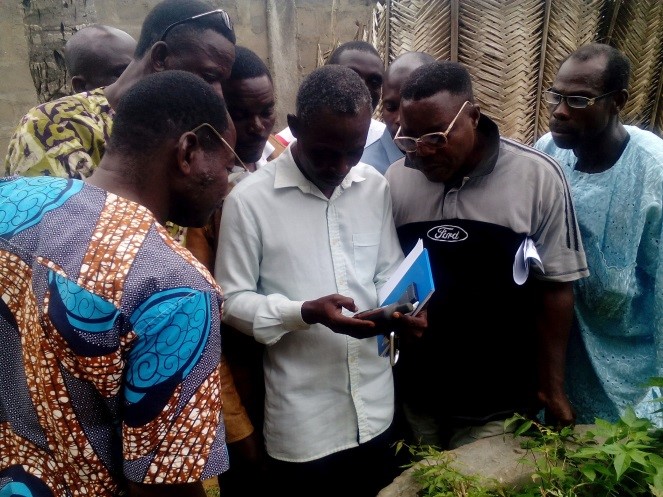
Verification and ground-thruthing of map information
GIZ/ProREDD
Training of cartographers
GIZ/ProREDD
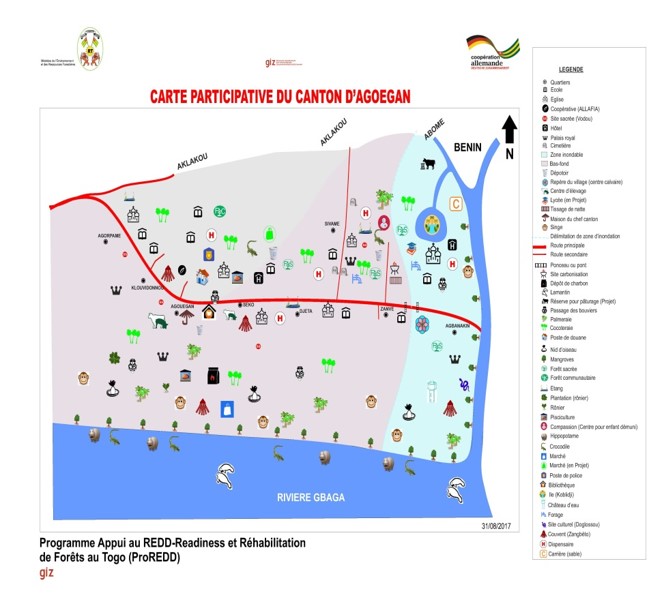
Example of a final participatory map
GIZ/ProREDD
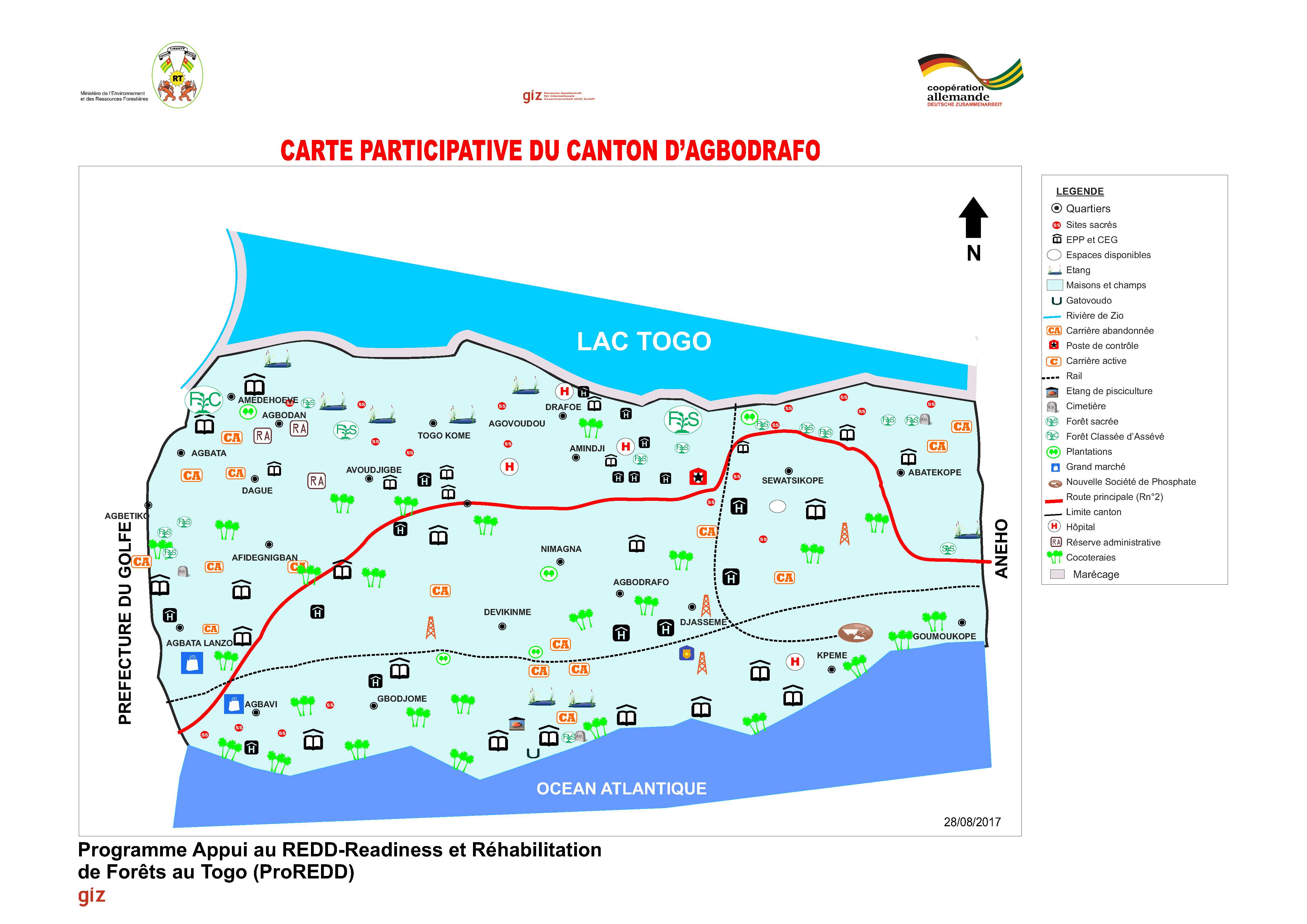
Final participatory map of Agbodrafo canton
GIZ/ProREDD
Participatory mapping was done by local communities in collaboration with the forestry administration and support by GIZ. It involved a true ‘cantonal’ approach by facilitating joint meetings between communities. They prepared their land use maps with guidance from advisors. This allowed to develop the relevant knowledge base for land use and restoration opportunities at regional scale and showed the importance of ecosystem connectivity in a landscape. Main steps of mapping:
- Preparation: Analysis & documentation of existing information, local visits to potential restoration sites, meetings with leaders of the prefecture and a launching workshop
- Awareness raising campaign in all 9 cantons and identification of two local cartographers per village (150 in total)
- Training of local cartographers in the development of participatory maps and the use of geoinformation tools including GPS
- Participatory mapping with 77 communities including joint identification of problems, mapping, verification and ground truthing of land use units by local experts and cartographers
- Development of final maps, validation and return of maps to local stakeholders
- Strong political commitment due to AFR100 pledge of Togo
- Appointment of an FLR Focal Point to the Director of Forest Resources (MERF)
- Availability of local experts, technical & financial support from the Togolese and German government
- Strong collaboration & knowledge exchange between projects at local, national and international level
- High community commitment and participation via existing prefectural, cantonal and village development committees & civil society organizations
- It was crucial to collaborate with community leaders and development committees from the beginning & use of their local knowledge about land resources and utilization
- Communities elaborated the land use maps on their own, while the project provided the framework conditions. This leveraged ownership, trust and acceptance between communities. It made them aware about the land boundaries & utilization types, condition and location of ecosystems (forests, agro-forests, coconut plantations, forest plantations, mangroves etc.) and land ownership types (public, community, private and sacred forests). It also enabled them to jointly identify environmental problems as the basis for identifying restoration priorities
- A combination of locally appropriate governance & communication processes (i.e. consensual approach, respect of customary rules) with technological approaches (GPS) was very successful