

Goal
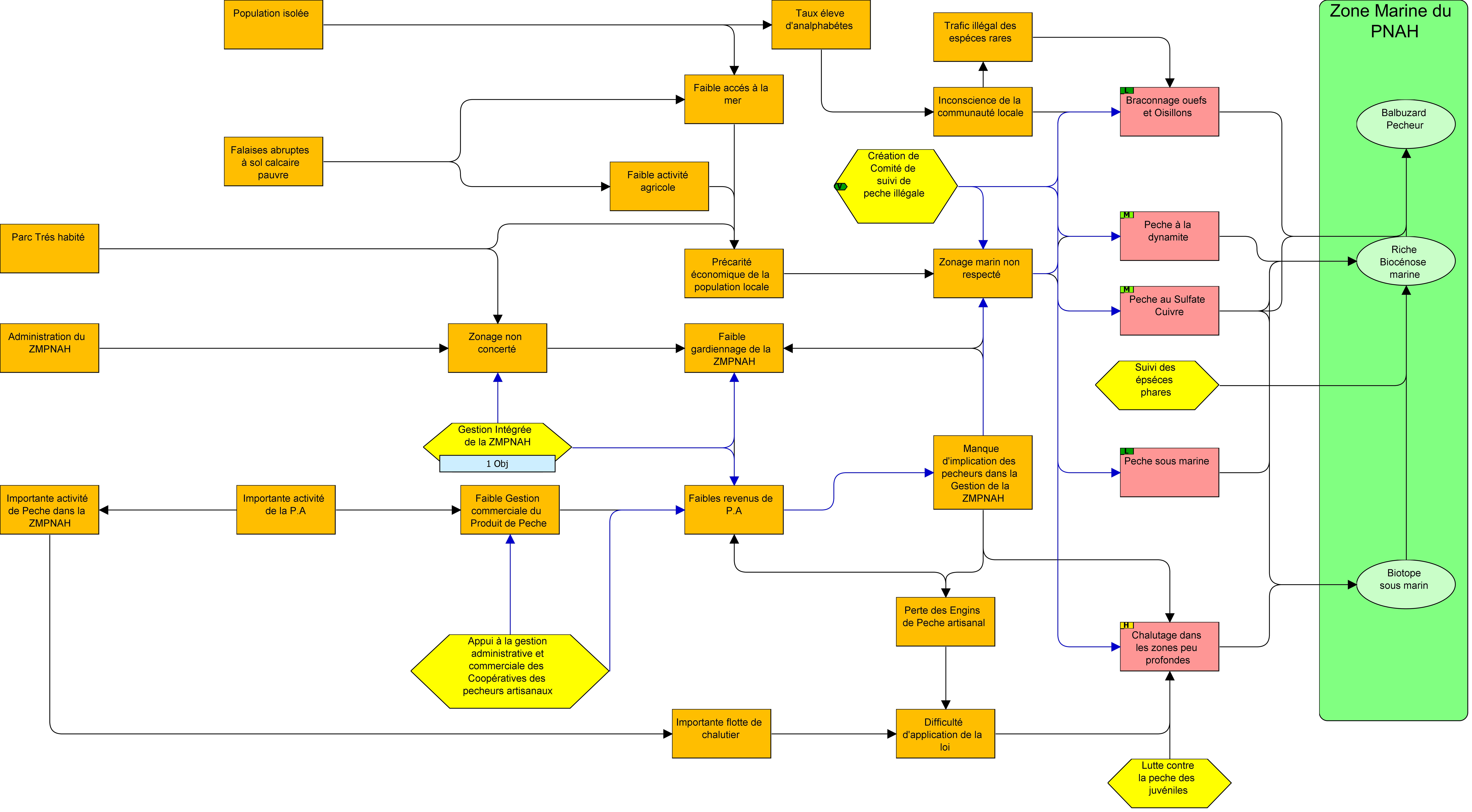
In order to engage the artisanal fishermen in natural resource conservation, the analysis carried out has included sociocultural, economic and ecological topics. The goal was to fill the lack of data to allow all the stakeholders to realize the initial decrease in biodiversity and the solutions brought by the project.
Process
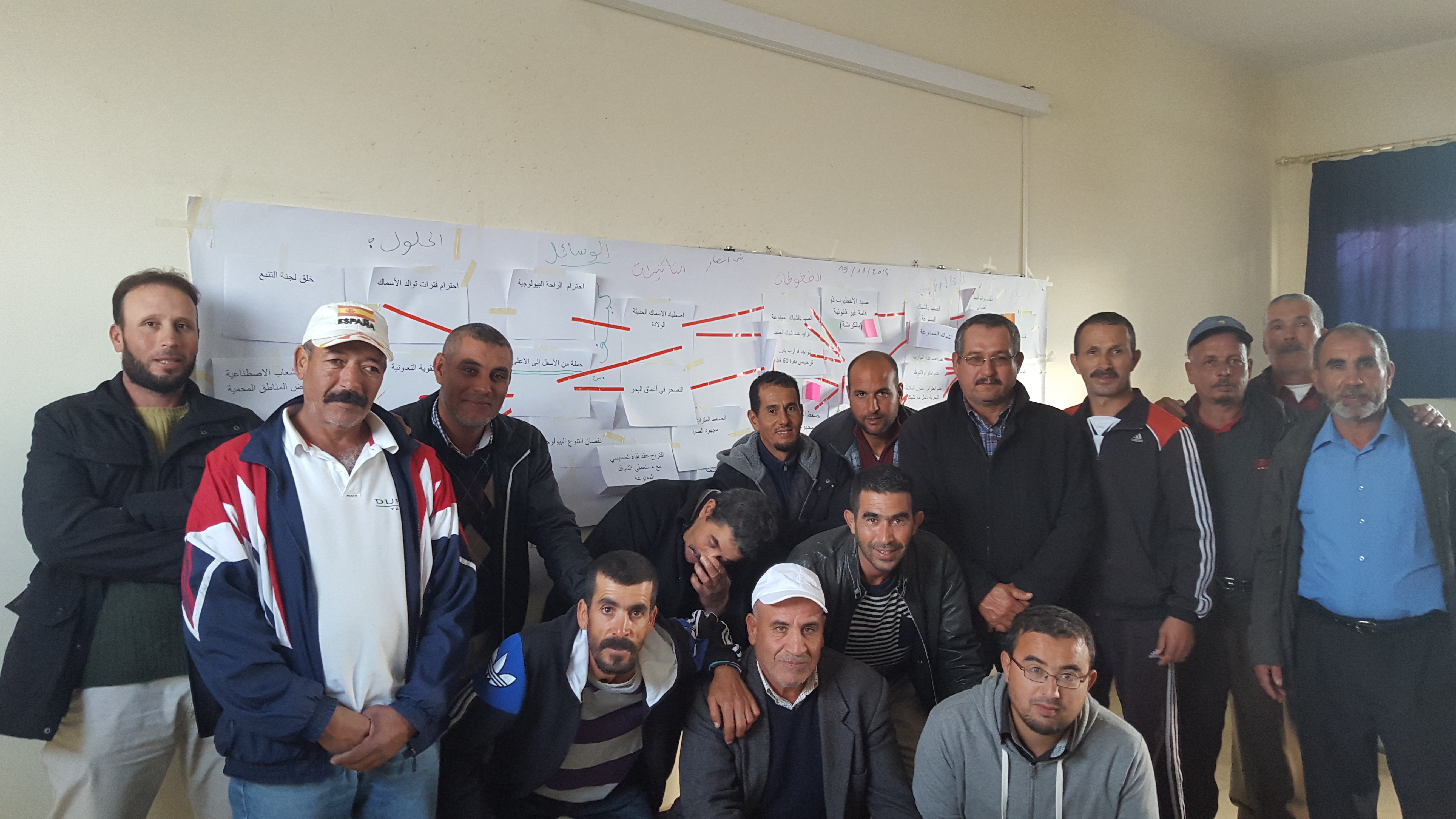
The participatory approach used by this study has allowed for all the stakeholders to accept the results.
The study was carried out in accordance with a systemic approach including several components:
- Scientific: “Sociocultural, economic, ecological indicators”
- Participatory: the study has not only involved the project holder, but also the stakeholders
- Prospective: the study has allowed to identify “current, potential and alternative scenarios”
The systemic analysis has led to an integrated action program for the sustainable management of the artisanal fisheries sector within the National Park’s marine area.
- Artisanal fishery represents one of the main economic activities in the region. As a sideline, it also improves farmers’ quality of life along the Mediterranean coastline.
- The main constraints to the artisanal fisheries’ economic growth have negative impacts on product quality, due to the lack of landing infrastructure and commercialization.
- The flotilla’s fragmentation and isolation, which the fishmongers take advantage of, does not allow the fishermen to work under satisfying conditions.
It is necessary to minimize the growth constraints on artisanal fisheries confined to the National Park’s fishing grounds. The reinforcement of fishing gear and equipment has to serve as a motivation for fishermen to stick to our integrated management plan.
Defining the artisanal fisheries sector remains an essential step in the process of implementing a commercial organization plan, which has to be subjected to future project propositions.
In the sociocultural plan, the fishing villages are confronted with a high rate of analphabetism. The fear of losing their jobs, translates itself to the high frequency of poaching, the use of dynamite or chemicals and illegal fishing.
It would be desirable to define a new zoning plan for the National Park’ marine area, which responds to the ecological conservation concerns and not only to those of fisheries resources. This would guarantee a sustainable development for a future approach of monitoring and participatory evaluation.