

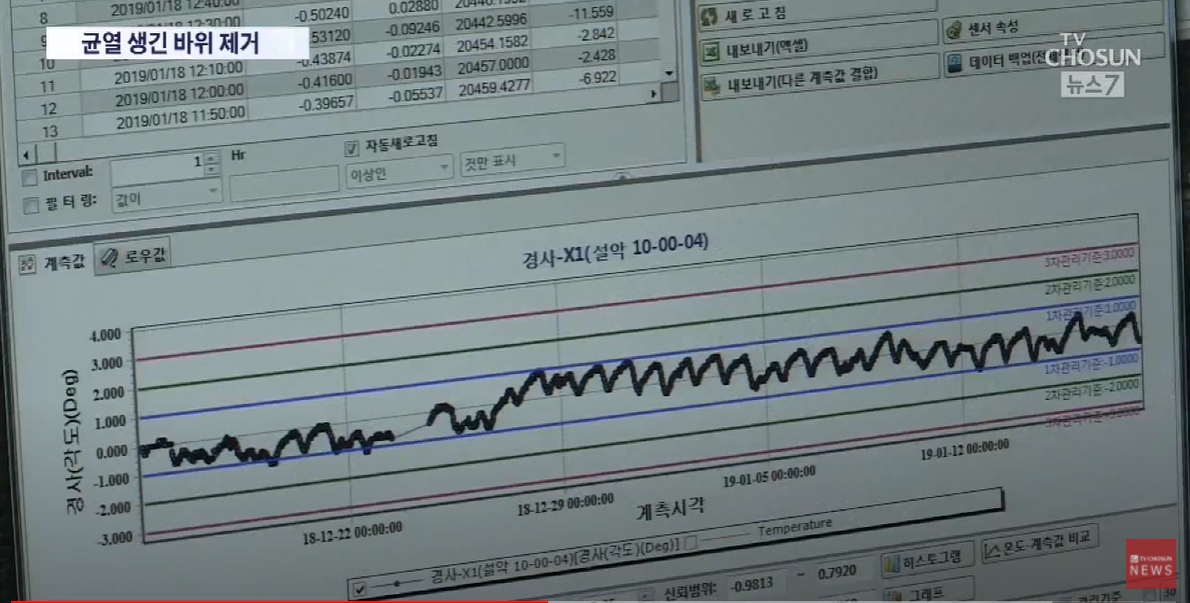
El medidor de grietas basado en IA para desprendimientos de rocas es un dispositivo que supervisa la aparición de desprendimientos de rocas y los desplazamientos de las grietas en tiempo real mediante la instalación de un sensor de observación en una zona de riesgo de desprendimiento de rocas situada a lo largo del sendero. Desde 2013, se han instalado medidores de grietas automáticos y manuales en laderas empinadas con alto riesgo de desprendimiento, y actualmente hay 525 unidades en funcionamiento en 174 ubicaciones. El dispositivo de medición de desprendimientos de rocas se divide en niveles de riesgo de "interés, precaución, alerta y grave". En la etapa de interés se realizan inspecciones periódicas y frecuentes. En la etapa de precaución, cuando las grietas son inferiores a 5 mm y a 2º, se refuerza la vigilancia. En las etapas de alerta, se prepara una investigación precisa y planes de acción para el desastre. En la etapa de gravedad, se controlan los caminos adyacentes y se aplican medidas de emergencia como la retirada de rocas desprendidas.
Antes de instalar el medidor de grietas basado en IA, se creó con antelación un equipo de investigación formado por geólogos y expertos en prevención de catástrofes para gestionar sistemáticamente los desprendimientos de rocas y las pendientes pronunciadas con el fin de investigar las zonas con riesgo de accidentes por desprendimientos de rocas a lo largo de los senderos de los parques nacionales. Además, las zonas con riesgo para la seguridad se clasificaron de la A a la E según el grado de riesgo, la pendiente y otras características geológicas, y se convirtieron en bases de datos.
En los últimos 10 años se han producido 81 desprendimientos de rocas en el parque nacional, con un balance de 3 muertos y 6 heridos, y daños materiales por valor de unos 2 100 millones de KRW. Sin embargo, desde 2018, cuando se utilizó el medidor de grietas basado en IA, no ha habido ninguna víctima mortal ni ningún herido entre los visitantes debido a desprendimientos de rocas. Además, se necesitaba mucho tiempo y trabajo para inspeccionar uno por uno todos los medidores de grietas instalados en todo el parque nacional. Con el tiempo ahorrado, los guardas del parque pueden concentrarse más en otras actividades de gestión del parque, lo que mejora enormemente la satisfacción interna.