


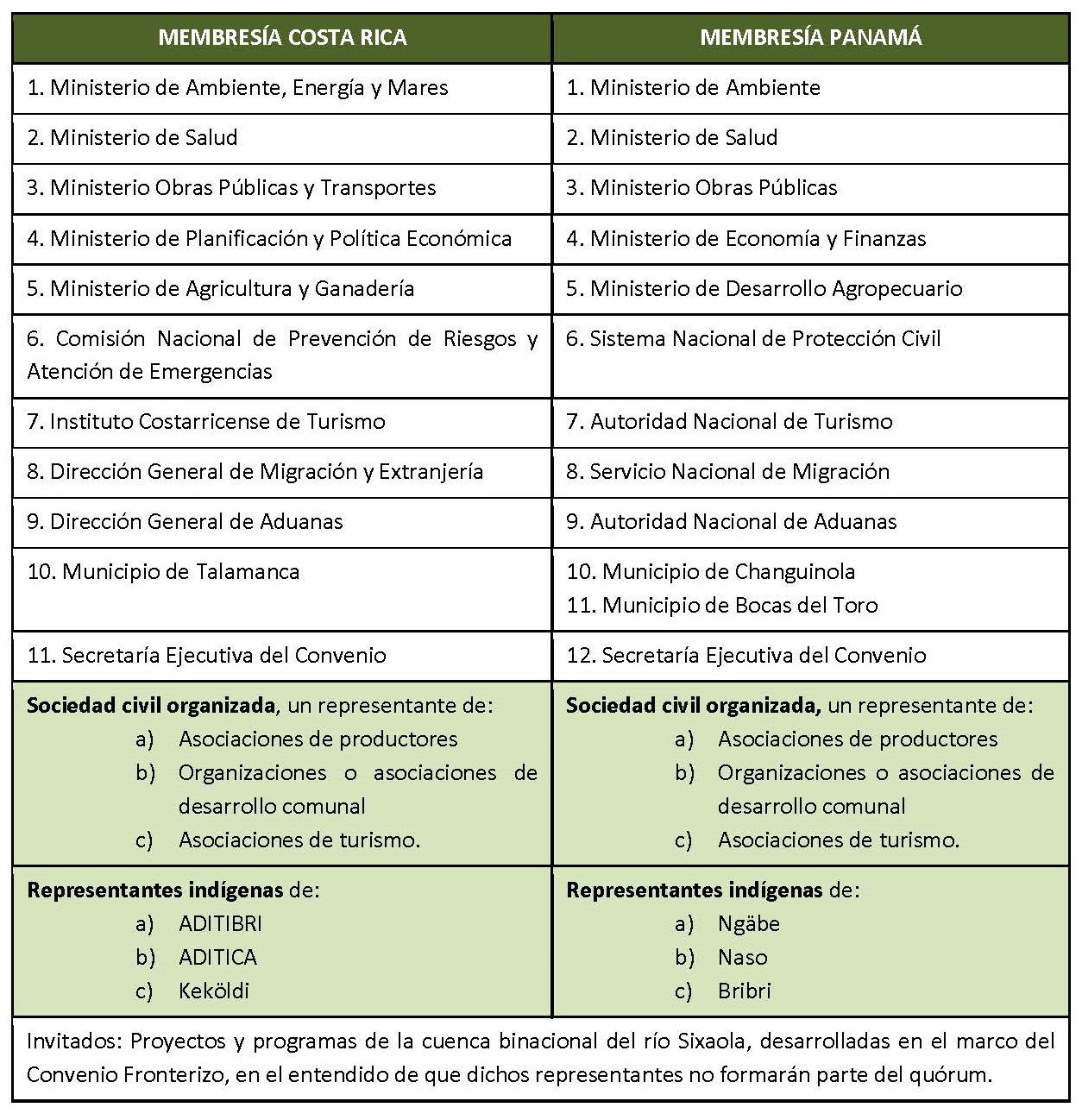
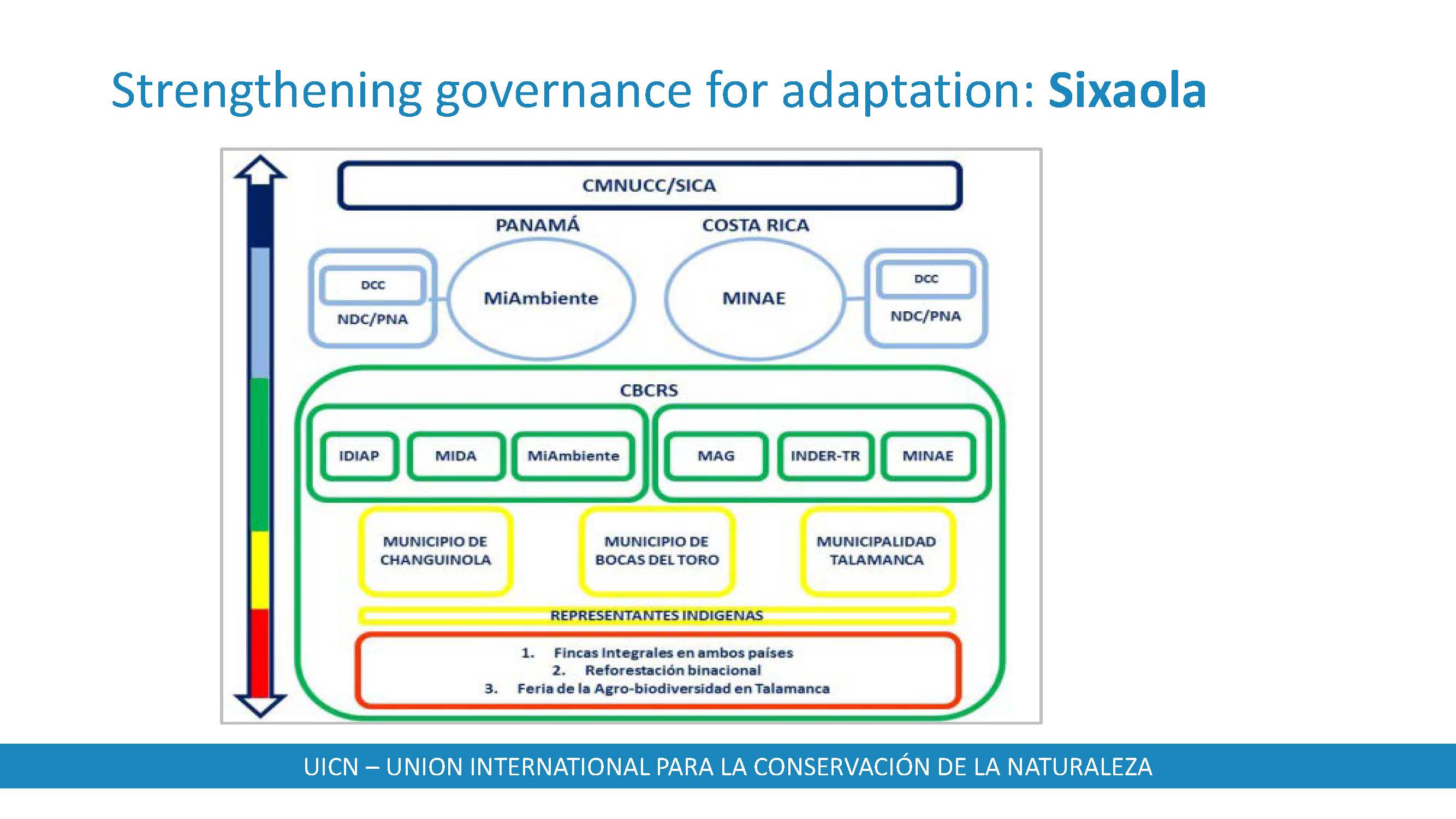
The Binational Commission of the Sixaola River Basin (CBCRS) functioned as a multidimensional (multisectoral and multilevel) governance platform for the basin. The CBCRS brings together representatives from different levels of government and sectors (including indigenous peoples and the local private sector of both countries) but needed to attain more effective vertical and horizontal integration. The preparation of the Strategic Plan for Transboundary Territorial Development (2017-2021) had the effect of fostering inter-institutional and inter-sectoral coordination and cooperation, forging dialogues on national frameworks and local needs, and promoting EbA.
At the local level Eba measures such as agricultural diversification with integral farms and reforestation actions were implemented. The aim was beyond individual impacts, to scale up lessons to the basin scale, such as:
- the CBCRS´s project portfolio
- the coordination of binational activities, such as Agrobiodiversity Fairs.
- the Biological Corridor Association of producers, which facilitated the exchange of experiences and peer-to-peer contacts (producers, municipalities)
- The prior existence of the CBCRS (since 2009), covered under the Cooperation Agreement for Border Development between Costa Rica and Panama, was a key enabling factor, since the purpose of this binational structure (achieving greater transboundary coordination and leadership for good governance and the integral development of the basin) was fully consistent with the objective of improving adaptation capacities to climate change impacts in the basin.
- Multidimensional governance is a central part of adaptive capacity. It is based on vertical integration of different stakeholders (local, subnational, national, regional), through the creation and/or strengthening of institutions where entities of multiple levels participate. It is combined with horizontal integration of sectoral authorities (public, private, civil society) in order to reduce isolated approaches in management and decision making, and allow mutual benefits and synergies between sectors and their adaptation needs to be identified.
- In adaptation, inclusion of municipalities is vital, since they have a mandate in territorial management, but also responsibilities in the implementation of national adaptation policies and programs (e.g. NDCs, NAPs).
- Peer exchanges (such as meetings between local governments) are an effective mean to awaken interest in the "natural solutions" offered by ecosystems.
- The articulation of project efforts across a territory is fundamental (e.g. between AVE and BRIDGE in Sixaola) in order to achieve greater impact through a coordinated work agenda.