Reviving High Quality Coffee to Stimulate Climate Adaptation in Smallholder Farming Communities in the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Uganda

The burgeoning specialty coffee sector in DRC offers a compelling example of how regenerative agricultural practices can enhance both environmental sustainability and market value. By focusing on producing high-quality coffee and implementing improved farming techniques, Congolese coffee farmers are tapping into a growing global demand for ethically sourced specialty coffee. Higher product standards command premium prices and contribute to increased economic resilience within local communities.
The Global Environment Facility (GEF) and Least Developed Countries Fund (LDCF) funded a partnership between the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), Nespresso, and TechnoServe through this project. Through Nespresso’s AAA Sustainable quality program, the project supported the sustainability of smallholder coffee farming households in South Kivu, DRC, while working to restore and revitalize degraded natural environments. Nespresso, TechnoServe, and DRC coffee farmers and cooperatives have partnered since 2019.
Context
Challenges addressed
Environmental:
- Improved land cover on smallholder coffee farms and surrounding landscapes to reduce soil erosion
- Increased climate resilience of farming households in DRC and Uganda
Social & Economic:
- Enhanced capacity of women to translate their participation into economic empowerment
- Improved livelihoods through access to the coffee supply chain and commitment for long term sourcing
- Improved household nutrition
Location
Process
Summary of the process
Climate change will likely bring negative impacts to the rain-fed agriculture sector in eastern DRC. Regenerative agriculture techniques can play an important role in helping enhance farmers’ resilience to climate change impacts that include more frequent flooding, erosion, and landslides, and thereby help protect their livelihoods. Women play an essential role in farming across DRC, yet many lack control over household income. This limits their access to resources like tools, seedlings, and training, making it harder for them to take part in restoration efforts. Without this support, women often miss out on the benefits that these initiatives bring—both financial and social.
Training on soil health, climate adaptation, shade management, and erosion control helped bring back biodiversity, improve soil health, and re-establish natural habitats. These efforts supported the sustainability of ecosystem functions in the eastern region near the Rwandan border, within the well-preserved landscapes surrounding Kahuzi-Biega National Park. Nespresso’s AAA Sustainable Quality Program aims to support coffee farmers to adapt to the challenges of climate change by adopting regenerative agricultural practices, while fostering gender inclusive opportunities.
Building Blocks
AAA Sustainability Quality Program
In order to increase resilience to climate change, coffee farming households need the knowledge and skills to apply regenerative agricultural practices that can increase biodiversity, enrich soil health, improve watersheds, and enhance ecosystem services.
Nespresso’s AAA Sustainable Quality Program empowers coffee farmers through three pillars: coffee quality, farm productivity, and social and environmental sustainability. Improvements in these areas can boost farmers’ financial security while also helping their communities and protecting nature.
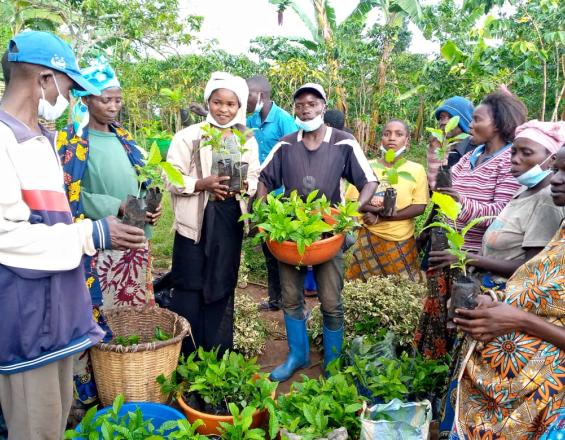
From July 2022 to April 2024, AAA agronomists — nearly half of them women — delivered monthly lessons to small, self-selected focal farmer groups of roughly 25 coffee farming households. Modules included a wide range of relevant topics, including regenerative agricultural topics (Coffee Pruning and Rejuvenation, Soil Health, Coffee Planting, and Shade Management and Climate Change), household nutrition topics (Nutrition Basics, and Establishment and Planting of Kitchen Gardens), and gender equality topics. With the establishment of demonstration plots, farmers learned through this hands-on, field-based training.
Enabling factors
- Evident, long-term interest and trusted relationships between Nespresso, TechnoServe, and farmers and cooperatives in DRC since 2019.
- Leveraging economic incentives through sustainable use of natural resources and respect for production standards.
- Close collaboration with local stakeholders: recruiting community members as AAA agronomists and focal farmers to train and model each practice leveraged their local knowledge to make the information relevant to the famers’ context.
Lesson learned
- Cooperation between private companies and small-scale farmers helped to empower producers and secure greater access to the large commodity markets for improved incomes and livelihoods.
- The AAA Academy was effective in supporting and amplifying knowledge of local farmers through training on regenerative agriculture, household nutrition, and gender equality.
- The level of support needed for smallholders is increasing as more producers are involved in the trade of fully washed specialty coffee from South Kivu.
Impacts
Environmental:
- The AAA Academy trained over 4,000 households on climate-resilient, regenerative agriculture practices in Kalehe, DRC, including nearly 5,000 farmers. The practices contribute to biodiversity, erosion control, improved watersheds, and enhanced ecosystem services among coffee-growing communities.
- Farmers in DRC received nearly 40,000 indigenous shade tree seedlings, enabling enhanced biodiversity and promoting the long-term sustainability of coffee farming landscapes.
Social & Economic:
- More than half of producers trained through the project were women, enhancing their economic empowerment by providing direct access to the global coffee supply chain.
- The AAA Academy used a gender safe spaces approach to support over 5,000 producers, including more than half women, to build an understanding of gender roles and how these create opportunities and constraints.
- Premium payments for sustainable coffee production provided an additional $43,200 in income for over 2,400 smallholder farmers in the DRC, ensuring market linkages for sustainable financing.
- Households participating in the program improved their access to nutrition through kitchen gardens, which led to reports of healthier diets and diversified sources of income.
Beneficiaries
Coffee producing communities in South Kivu, and coffee processing enterprises. Women were targeted as direct beneficiaries in all aspects of implementation of the AAA Academy.
Sustainable Development Goals
Story
Climate resilient coffee farming changing lives in DRC. Antoinette Shabanyere and Munyangali Mutugari's stories are shared in full in this blog here.