Achieving multi-dimensional governance for adaptation
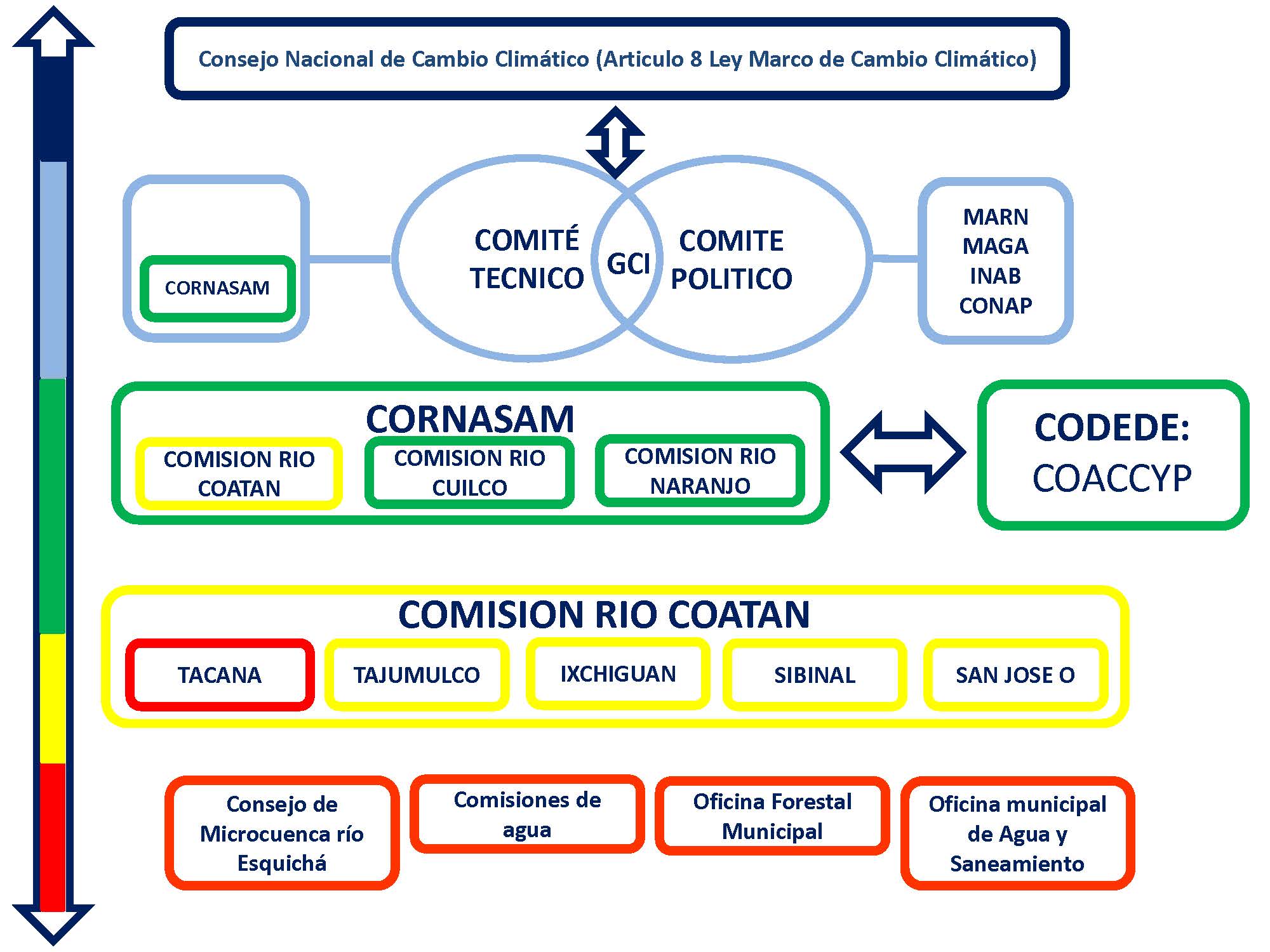
Instancias de gobernanza en múltiples niveles
IUCN
Showcasing the work of the Esquichá Micro-basin Council
IUCN @ Milton Navarro
The Esquichá River Micro-basin Council acts as a platform for dialogue, advocacy, capacity building and appropriation of lessons learned and tools; therefore, it is a key means for up-scaling EbA to different levels. With a view of vertical scaling, lessons of its work have influenced different levels:
- the Municipality of Tacaná that will include EbA measures into municipal planning.
- the Coatán River Council (only with national Guatemalan authorities) which facilitates inter-sectoral cooperation and management with a basin-wide vision, beyond the mere political-administrative sphere.
- the Coordinator of Natural Resources and Environment of San Marcos Department (CORNASAM). CORNASAM coordinates the efforts of governmental actors and NGOs, as well as the municipalities of the Department of San Marcos.
- the National Secretary of Planning (SEGEPLAN) in order to improve guidelines given to municipalites planning.
- the Ministry of Environment (MARN), that is using lessons learnt to scale up a Green Climate Fund project that implements EbA measures.
- the Forest Institute (INAB)
Further work is needed to have a binational coordiantion of the Coatán river basin, shared among Guatemala and Mexico to have a higher impact on the benefits of EbA.
- Using traditional knowledge and local experiences to select EbA measures, enabling the application of EbA
- The participatory structure of the Esquichá River Micro-basin Council, which is made up of the Community Development Councils of local communities, fostered the possibility of working in an organized manner and influencing higher levels (e.g. Municipal Councils).
- The existence of CORNASAM since 2004 was an enabling factor, since the purpose of this platform aligns well with the objective of improving adaptation capacities in the micro-basin
- Platforms such as CORNASAM are ideal for strengthening adaptation governance, since they bring together national and sub-national institutions and authorities from different sectors (vertical integration). CORNASAM seeks to reduce isolated approaches and aims to facilitate the identification of mutual benefits and synergies between sectors and their adaptation needs (horizontal integration).
- Governance for EbA must promote open, equitable, respectful, and effective participation, so that planning and decision-making processes are enriched by the participation and the results are accepted by all parties involved.