Addressing power dynamics and promoting engagement in collective action
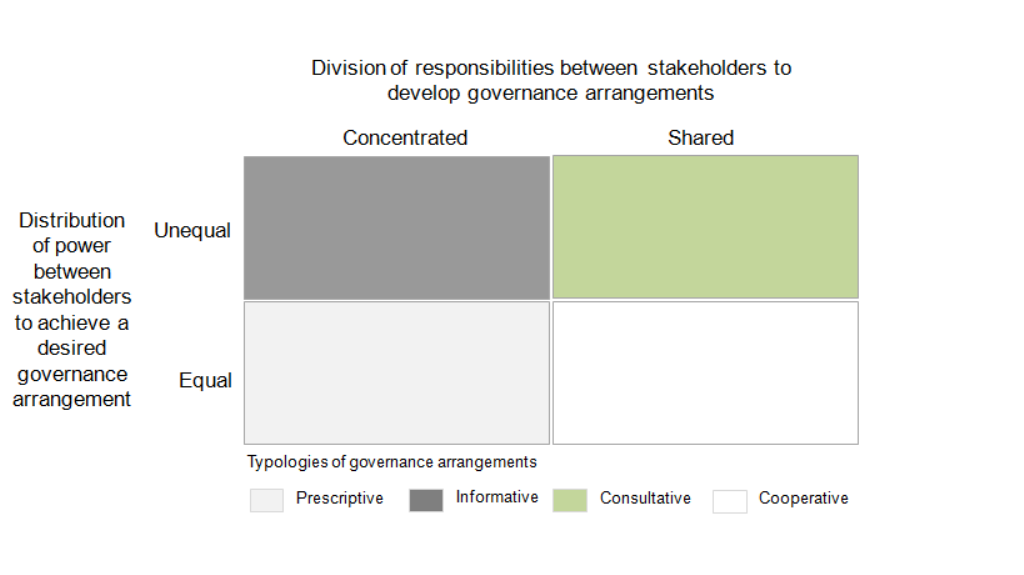
The analytical tool to guide participation assessment of governance arrangements in the Sierra de Guadarrama National Park (adapted from López-Rodríguez et al. 2020)
María D. López Rodríguez
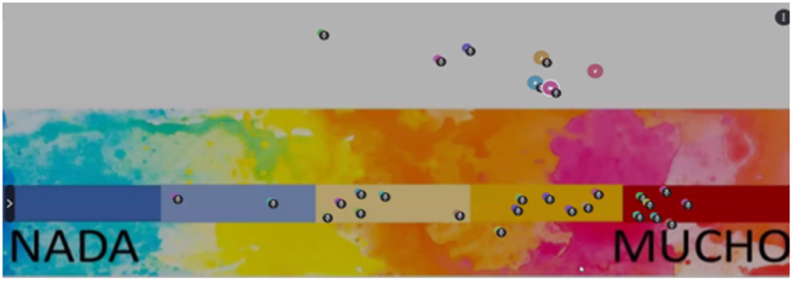
The “barometer of power”, one of the theatre-based facilitation techniques to address power dynamics between stakeholders used in a virtual workshop in the Sierra de Guadarrama National Park
Maria Heras
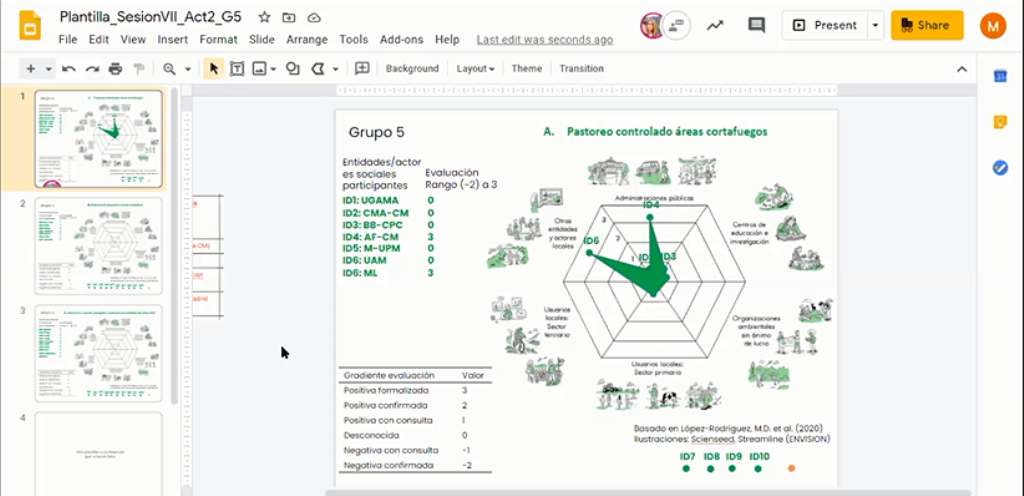
Screenshot of the context-specific boundary object to call for collective action used in an online workshop in the Sierra de Guadarrama National Park
María D. López Rodríguez
These three decision-making tools were crucial to address power dynamics and promote stakeholders' participation and engagement in collective action in the National Park:
- An analytical tool to characterize types of governance arrangements in the protected area. Formal and informal governance arrangements were classified in terms of stakeholders’ responsibility (shared vs. concentrated) and influence (equal vs. unequal) into four types: prescriptive, informative, consultative, and cooperative. By applying this tool in the National Park we identified challenges for more socially inclusive conservation while enhancing existing participatory mechanisms and delineating new ones;
- Theatre-based facilitation techniques to address power dynamics between stakeholders. By using them in a virtual workshop, participants deliberated on their roles and power relations around conservation governance and how these may be reconciled to improve collaboration;
- A context-specific boundary object to facilitate collective action for conservation governance. Using this graphical tool in a workshop, participants assessed their level of willingness to put several strategies into practice. The tool visualized the results graphically as a proxy of the potential willingness to move from theory to practice.
- The analytical tool to characterize governance arrangements requires data collection about the existing decision-making mechanisms behind each arrangement identified, the stakeholders engaged and how they are engaged;
- The art-based approaches and context-specific boundary object require a process based on co-learning and knowledge co-production approaches through which stakeholders deliberate on power dynamics, conservation challenges and define collaborative strategies to address them.
- Analyzing both formal and informal-based governance arrangements serves as a means to understand how participation in conservation decision-making is actually shaped within protected areas governance and how to improve stakeholder engagement given the context;
- It is important to consider informal governance mechanisms to understand potential trade-offs because they can lead to both positive and negative outcomes for conservation;
- Stakeholders’ responsibility and influence are key analytical axes to delineate participatory mechanisms in order to identify opportunities for more socially inclusive conservation;
- Art-based methods are useful to incorporate power relations aspects into conservation debates;
- Elucidating unequal relations for conservation governance offers opportunities to clarify stakeholders’ roles and their responsibilities and facilitate a better understanding of how these may be reconciled to improve collaboration;
- The assessment of stakeholders’ willingness to be involved in putting the strategies into practice is a crucial factor to guide collective action.