Gagner de l'argent avec des déchets
Pour répondre à la nécessité de gérer correctement les déchets de la pêche, des membres de la communauté de pêcheurs El Caracol à Guasave, dans l'État de Sinaloa, ont fondé Grupo Crustil, une petite entreprise de transformation. Le groupe utilise les déchets de la pêche artisanale pour produire de la farine de poisson. Le processus crée des opportunités de génération de revenus alternatifs, maximise l'utilisation des produits et atténue les impacts sur l'environnement.
Contexte
Défis à relever
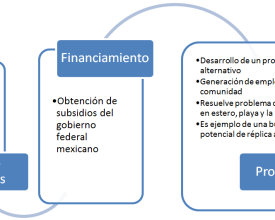
- Les déchets de la pêche polluent les écosystèmes et la stratégie de gestion des déchets fait défaut
- Accumulation des déchets de la pêche dans les estuaires, les canaux et sur les plages
- Manque de possibilités d'emploi dans la communauté
- Manque de sensibilisation de la communauté au traitement approprié des déchets de la pêche
Emplacement
Traiter
Résumé du processus
à confirmer
Blocs de construction
Plan d'entreprise pour la production de farine de poisson
Un plan d'affaires pour la transformation des déchets de poissons et de crevettes en farine de poisson est élaboré, définissant la conception de l'entreprise et déterminant ses coûts. Le plan comprend le concept des opérations, la structure organisationnelle, la conception du système, les processus de production, les modules de formation, le marketing et les ventes, ainsi qu'une analyse de faisabilité.
Facteurs favorables
- Définition de l'organisation, de l'administration et du fonctionnement du projet
- Assistance technique à la préparation du plan d'affaires
- Renforcement des capacités du groupe qui gère le projet
Leçon apprise
- Le plan d'affaires est la base de la mise en œuvre et de l'administration du projet.
- La définition de la faisabilité du projet doit tenir compte des conditions locales.
- Définir le potentiel du marché et les processus de commercialisation
Fonds d'amorçage du gouvernement
Pour recevoir un financement du gouvernement fédéral de la part de la Commission nationale des zones protégées et d'autres bailleurs de fonds, l'entreprise doit démontrer ses avantages environnementaux et sociaux (tels que détaillés dans le plan d'affaires) ainsi que sa capacité à être autosuffisante dans un laps de temps donné. La subvention est utilisée pour acheter l'équipement nécessaire et former le personnel.
Facteurs favorables
Les subventions accordées par le gouvernement mexicain ont permis d'engager une équipe et de renforcer les capacités de l'organe de gestion.
Leçon apprise
- Il est important d'explorer différentes sources potentielles de financement.
- Le projet doit montrer qu'il peut être autonome à un certain stade et qu'il ne dépendra pas indéfiniment de subventions pour sa mise en œuvre.
Entreprise de transformation
L'usine de transformation à petite échelle produit de la farine de poisson et de crevettes. Le produit est utilisé comme aliment pour la volaille, les porcs, le bétail ou les poissons et crevettes d'élevage, et comme engrais organique. Il est vendu sur les marchés locaux et régionaux.
Facteurs favorables
- Les ressources (1 000 tonnes de déchets de pêche) étaient disponibles sans coût supplémentaire.
- Marché local et infranational existant
Leçon apprise
- L'organe de gestion a pris conscience de l'importance du développement des capacités afin de fabriquer des produits de haute qualité qui répondent aux normes de qualité communes.
- Il est possible de mettre en œuvre des projets qui génèrent des revenus tout en ayant des effets sociaux et environnementaux positifs.
- Le projet a été présenté à d'autres pêcheurs et communautés du golfe de Californie, au Mexique, et l'organe de gestion a été invité à conseiller la reproduction et la mise en œuvre de cette approche dans d'autres régions.
Diffusion et formation
L'entreprise contribue à sensibiliser la communauté à la nécessité de gérer correctement les déchets de la pêche en collectant leurs déchets, qui sont ensuite ramassés par le personnel du Grupo Crustil. Une formation à la production de farine de poisson et de crevettes est dispensée afin d'améliorer les compétences du personnel. L'entreprise est également présentée à d'autres communautés de la région afin de faciliter sa reproduction.
Facteurs favorables
à confirmer
Leçon apprise
à confirmer
Impacts
- L'accumulation de déchets de pêche dans l'estuaire, les canaux et la plage est en baisse. Le Grupo Crustil traite environ 1 000 tonnes de déchets par an ! Cela réduit également la contamination et le risque d'infections et de maladies.
- En outre, l'entreprise et ses activités ont entraîné un changement d'attitude des membres de la communauté à l'égard de la réduction de la contamination de l'estuaire, des canaux et de la plage. La population locale a été sensibilisée à l'importance d'une gestion durable des déchets de la pêche et à son impact sur sa propre santé.
- Les membres du groupe qui gèrent le projet ne sont plus pêcheurs mais consacrent tout leur temps à l'entreprise. Cela génère une activité alternative et productive avec la création de nouvelles opportunités d'emploi pour l'ensemble de la communauté : 3 employés en basse saison et entre 10 et 15 employés en haute saison.
Bénéficiaires
Les femmes et les hommes employés dans le cadre du projet ainsi que la communauté locale.
Objectifs de développement durable
Histoire
à confirmer