The manual screening of 532 Hainan gibbon acoustic sample has been completed, including those obtained during tracking and observation of gibbons using a portable recorder and those obtained using an automated recorder. During the screening process, three recording qualities were initially categorized, namely hight, medium, and low. 44 high-quality recordings from seven individual callers were obtained. The seven individual callers were GAM1、GBM1、GBSA、GCM1、GCM2、GDM1、GEM1, where the letter after “G” represents the family group number and the letter after “M/S” represents the individual number of adult male/subadult male individual number. Only about 40.9% of the recordings were made manually. The raw files of all automated recordings were provided by the team of professor Wang Jichao, and the related data were backed up at Hainan Institute of National Park.
Mel-frequency cepstrum coefficients (MFCCs) is a method of extracting frequency envelope features by cepstrum after weakening the high-frenquency information on the basis of human hearing[1], which has a wide range of applications in the field of human and bioacoustics. In this study, MFCCs and the first-order and second-order differences (△、△2) are used to achieve automated feature extraction.
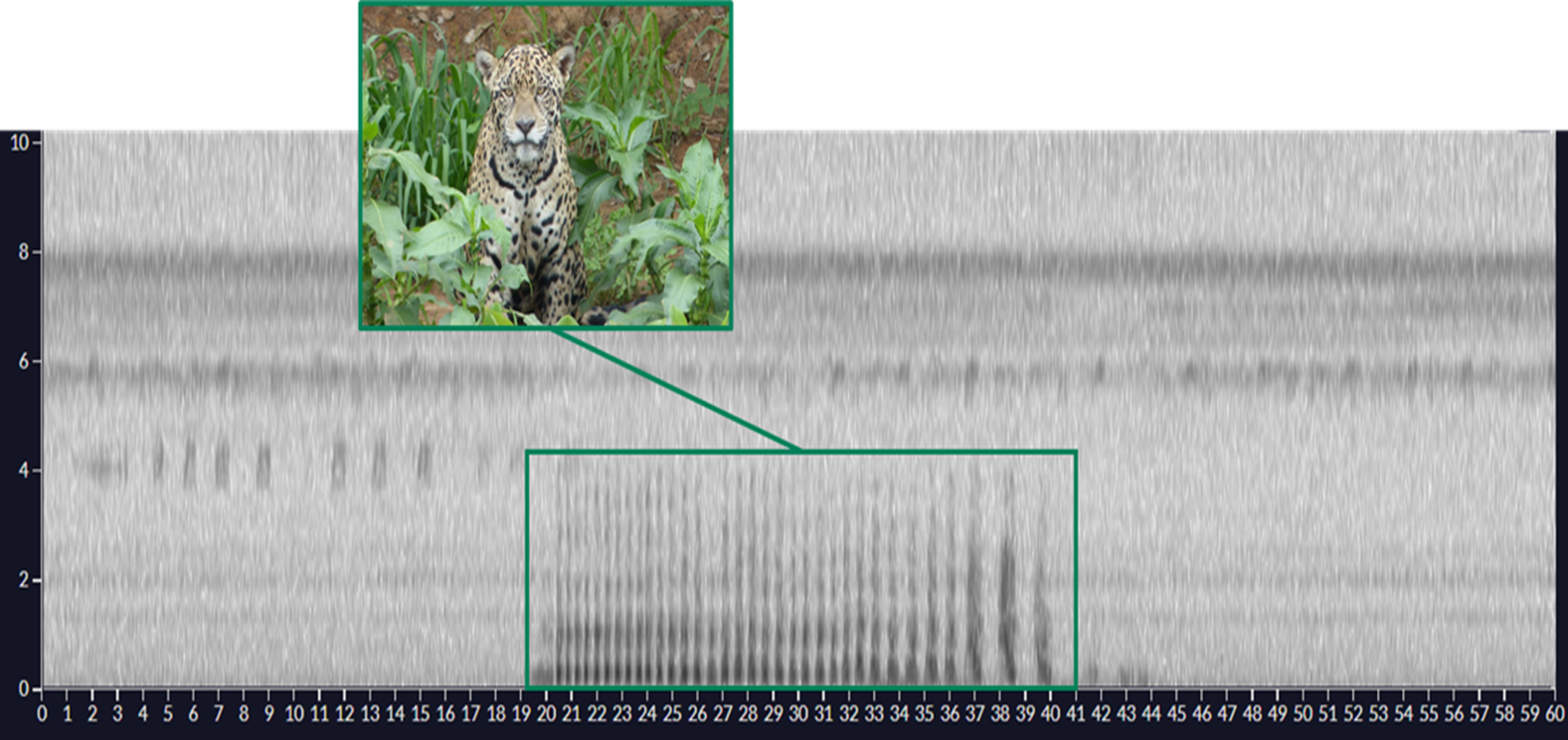
5 signature notes of the male Hainan gibbon have been identified (Fig.1), including boom note, aa note, pre-modulated note, modulated-R0 note, and modulated-R1 note.
According to the acoustic niche hypothesis, the calls of different species are differentiated in the time and frequency domains (see Fig. 2), so extracting features in a specific frequency range can greatly reduce the influence of noise, and the smaller the frequency range delineated, the more likely it is that more noise will be excluded. In addition, when the structure of each minimum recognition units (MRUs) is the same, the difficulty of recognition is greatly reduced.
In view of the above situation, in this phase of the research, we tried (1) applying pre only and (2) using pre + n×mR0 as MRU, respectively, and comparing the classification results so as to determine the most appropriate feature extraction in the subsequent work. In the case of voice annotation, all the above steps can be implemented automatically by R language code.