Taking stock of the existing Blue Economy
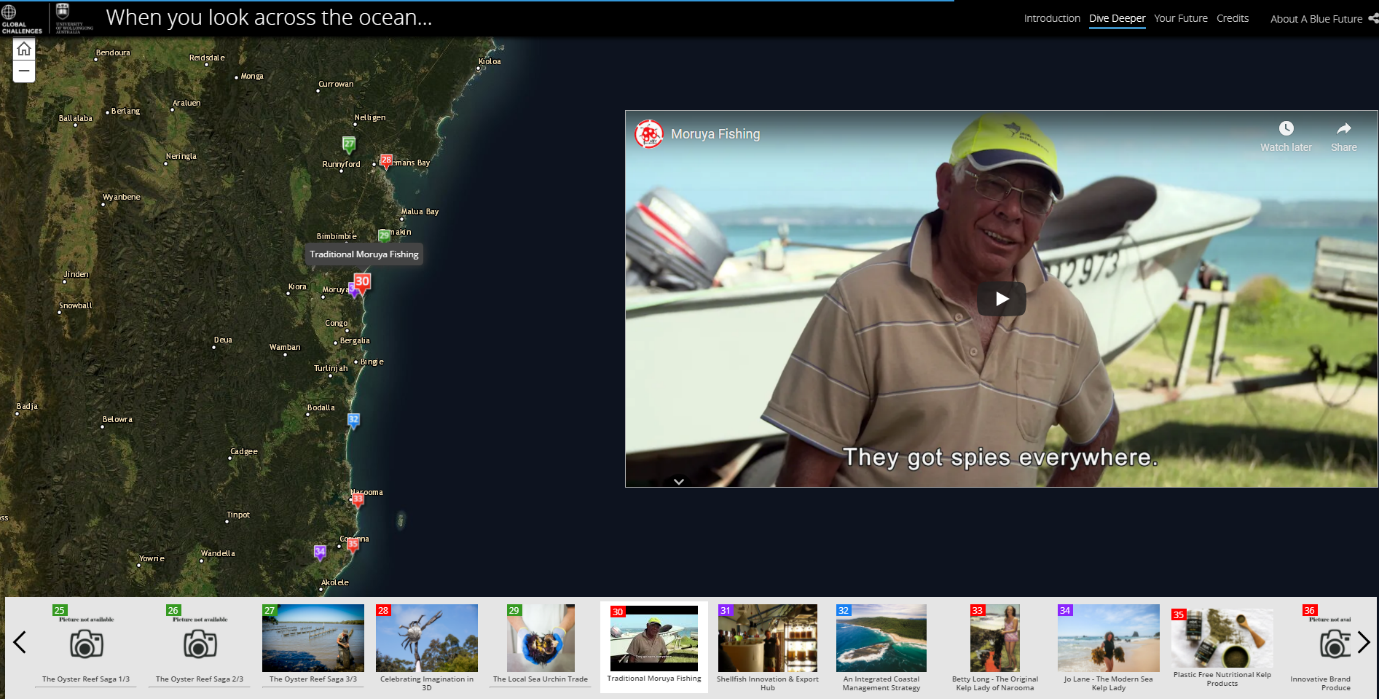
The storymap interface, centred on a pin of an indigenous fishing enterprise in Moruya, NSW
UoW
An example image from the storymap: Cruise tourism
Open source
An example image from the storymap: 3D seawalls
Open source
Before embarking on a journey to build a community based approach to a Blue Economy we felt it was important to first understand where we had come from and where we are now. We examined the historical role of maritime businesses on the NSW South Coast and the existing economic, social and cultural relationships of South Coast communities with the ocean. The result was a Blue Futures ‘Story map’ which details the diverse ways in which businesses, community groups and individuals engage with the ocean in our region.
When ‘taking stock’ of a region’s blue economy potential, the story map design ensured that no one social, environmental or economic angle was prioritized over another. Instead, space became the organizing principle, enabling users to scroll around the map to learn about what was important to the blue economy around them. In practice, this meant that employment statistics, historic coastal artworks and ocean governance examples appeared alongside clean ocean tech startups and established marine industries. The map brings these data into conversation with each other in the mind of the viewer, purely by their spatial proximity. This is an important first step in raising the profile of cultural and social data for developing blue economy solutions, which are often overlooked in favour of quantifiable statistics.
This building block was enabled by a multidisciplinary team committed to working across traditional disciplinary silos. Artists worked with geographers, economists and environmental scientists to gather together a breadth of visual and textual materials for inclusion in the story map.
We underestimated how long the storymapping process would take. Substantial time was needed to bring together digital resources, rights for image use (both from companies, artists and museums/archives) and for trialing different story map styles to best suit the project scale and range of sources.
Collating diverse data sources together in a publically accessible and easy to navigate story map gave this building block a larger audience both locally and globally than a traditional written report or textual media release. The story map educated diverse audiences about the ‘blue economy’ and ‘blue future’ concepts which would be viewed by many as otherwise amorphous or niche ideas, at a distance from their everyday lives.