Breeding and Husbandry Techniques for the Chinese Giant Salamander (Andrias davidianus)
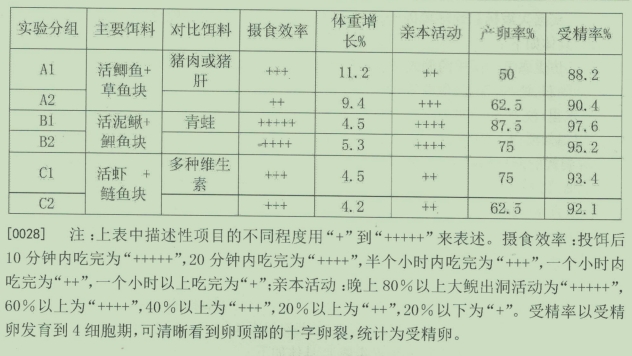
Bait Comparison Experiment Table
Hunan Province Giant Salamander Rescue Center
Breeding technology for broodstock selection involves choosing individuals of different sexes and origins from the same region as parents. The feed suitable for breeding should be diversified, mainly consisting of feed that is high in protein, low in fat, low in calories, and rich in trace elements. One month before and after the breeding period, feed that is high in protein, high in fat, and high in calories should be provided.
Feed selection and proportioning experiments involve feeding different aquaculture ponds with different feeds, and conducting trials with different combinations to determine the optimal feed plan and the best nutritional structure for the ecological breeding of the giant salamander. By mastering the most suitable feed and nutritional combination for different periods of the giant salamander, the sperm quality of male broodstock can be improved, and the egg-bearing capacity of female broodstock can be increased.
Essential factors:
1. Avoid inbreeding. Selecting parents of different sexes and origins from the same region can effectively prevent inbreeding;
2. Choice of feed. Choose feeds that are more easily obtained and have comprehensive nutritional components, such as grass carp, silver carp, loach, shrimp, frogs, pork, and pig liver, etc.
3. Feed processing. Live fish should be freshly killed, and inedible parts such as heads, bones, and spines should be removed; pork and other meats should have fat (if any) removed and cut into long strips weighing about 50 to 100 grams. Dead bait should be soaked in a 30% saltwater solution for 10 minutes; live bait should be soaked in a 2-3 ppm chlorine dioxide solution for 10 minutes.
4. Feeding of feed. Feed should be provided on a regular schedule, with consistent quality, and in fixed quantities. Dead bait should be offered every three days, around 6 pm, with the standard that it should be consumed within one hour. Live bait should be fed at 5% of the total weight of the giant salamanders in each area, with discretion to increase the amount as appropriate.
By recording the feeding, weight gain, activity, ovulation, and fertilization of the giant salamander (see attached figures). It was found that Group B had a significantly higher feeding efficiency than the other two groups, indicating that the giant salamander will turn to dead bait with lower predation difficulty when hunting live prey is challenging. Data from Group A show that the giant salamander gains weight quickly when fed a diet high in protein and fat for a long period, but has a low ovulation and fertilization rate. In combination with the analysis of the main nutritional components of various baits, it is suitable for the giant salamander's bait to be diversified, mainly consisting of baits that are high in protein, low in fat, low in calories, and rich in trace elements, such as various fish, loach, shrimp, crabs, frogs, etc. One month before and after the breeding period, appropriately high protein, high fat, and high calorie foods can be fed, such as various fish and poultry meat and internal organs, which is beneficial for the giant salamander to accumulate energy before breeding and to recover and overwinter after breeding.