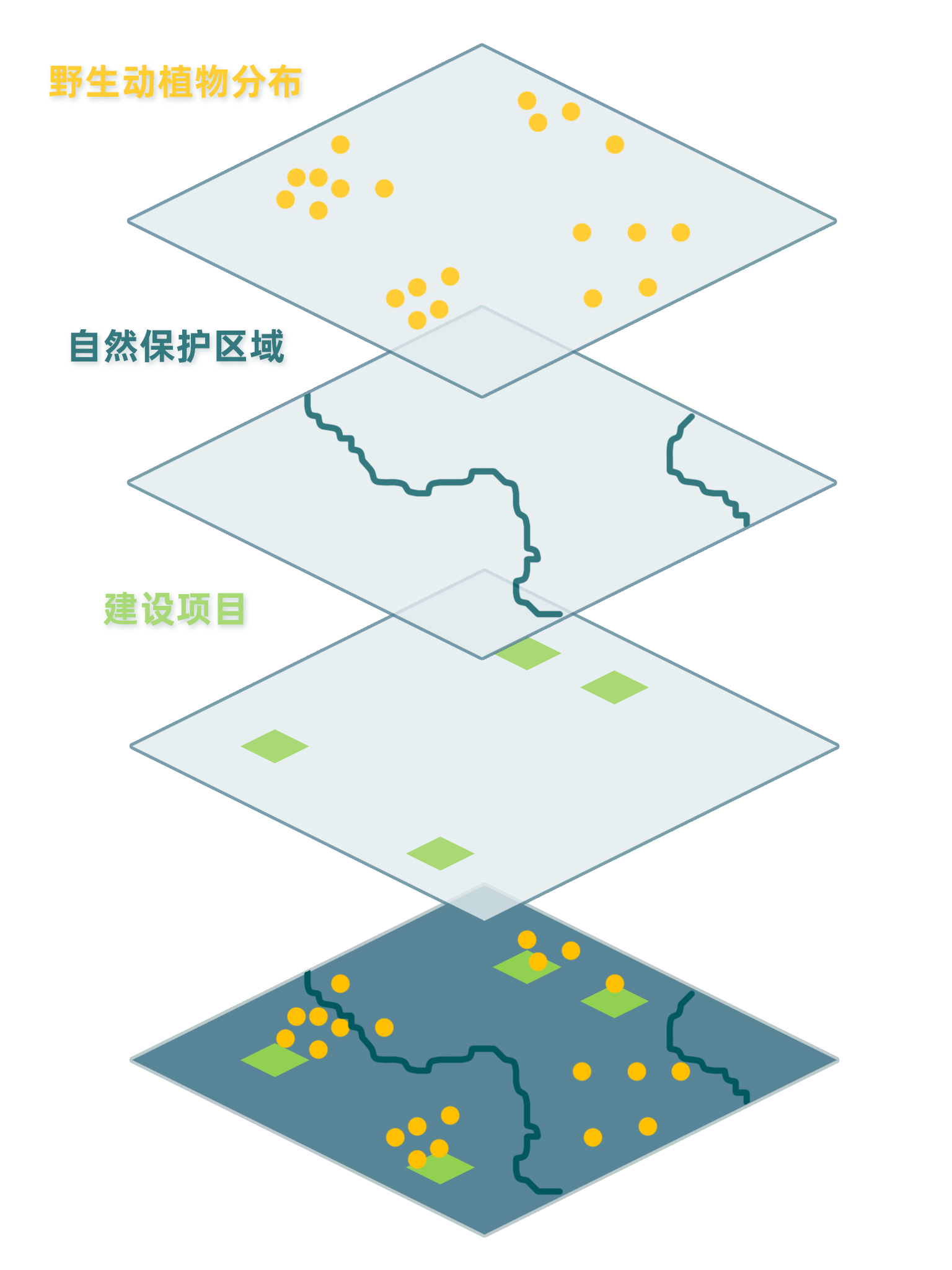
Years of research and conservation practices have not only stressed the importance of biodiversity data but also revealed the flaws of current workflow, ranging from inefficient data management, lack of data integration, to limited public-accessible data applications. Moreover, such workflow is mainly man-powered and often involves a lot of repetitive work, taking up huge amount of conservationists’ time.
Following the rapid development of technology, we have gradually realized the potential of technology to bring solutions to our “pain points” for long. In order to utilize technology tools in places in most needs, a systematic review and analysis of the current workflow was conducted to identify bottlenecks with high priorities and the possible solutions. The contemplation began in May 2018 and was materialized starting from Jun 2019 after potential technical partners emerged. Based on the systematic workflow analysis and close partnership, we made a step-by-step plan, aiming at developing modules one by one, considering our limited resource and manpower (e.g., from community-based camera trap monitoring assistant app, to BiA tool, to citizen science data visualization platform, to camera trap data management system).